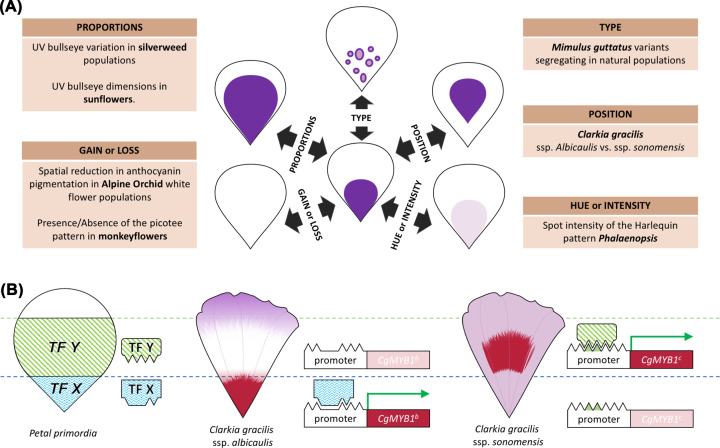
Figure 4. Mechanisms associated with pigmentation pattern evolution.
(A) Possible modifications affecting petal pigmentation patterns (centre) and examples from the literature corresponding to each case. (B) A shift in petal spot position in Clarkia gracilis occurred following mutation(s) in the regulatory region of CgMYB1: expression of an ancestral CgMYB1b allele is thought to have been activated by an unknown TF, TF X, restricted to the petal base. This results in the production of basal petal red spots similar to the one of subspecies albicaulis. Mutations in the promoter of CgMYB1 would have resulted in the loss of TF X cis-elements, but a gain of binding sites for another unidentified activator, TF Y, expressed in the middle of the petal. The new allele CgMYB1c is capable of triggering spot production higher up along the proximo-distal axis of the sonomensis subspecies.