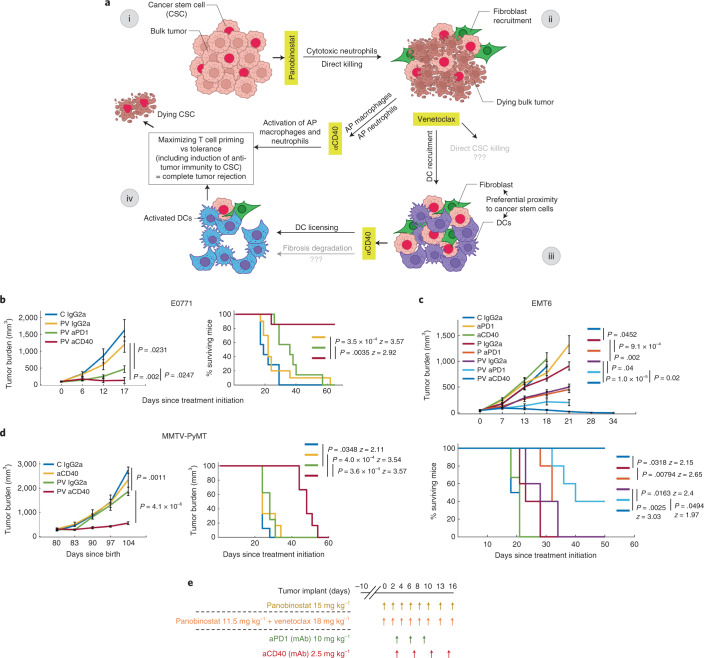
Fig. 6. Efficacy of the triple combination of panobinostat, venetoclax and anti-CD40 immunotherapy in mammary carcinoma and rationale for the combination.
a, Hypothetical model of response for panobinostat/venetoclax/anti-CD40 triple combination treatment efficacy in breast cancer. In brief, the tumor is composed of bulk tumor and CSCs (i). Panobinostat induces immunogenic cell death of the bulk tumor while CSCs remain resistant in the TME (ii). Venetoclax induces recruitment of DCs in proximity to CSCs (iii). We hypothesize that, if CD40 ligation induces licensing of DCs, which captured and processed antigen from neighboring CSCs, the triple combination potentiates CSC-specific anti-tumor immunity, leading to complete tumor rejection (iv). b–d, Tumor burden measurements (left and top graphs) and survival rate (right and bottom graphs; 100% to 0%) over time in E0771 (b); EMT6 (c); and orthotopically induced tumor-bearing mice and MMTV-PyMT mice with spontaneously growing tumors (d). C, control; P, panobinostat, PV, panobinostat/venetoclax combination. For tumor burden, line graphs are mean ± s.e.m. per timepoint; n = 7–10 mice, 6–12 tumors and 6–8 mice per group in b, c and d, respectively. Significance was calculated by unpaired two-tailed t-test with equal variance. For survival rate, P value was calculated by log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test. e, Treatment dose and schedule for b,c,d. Schematics in a was partly generated with BioRender. mAb, monoclonal antibody.