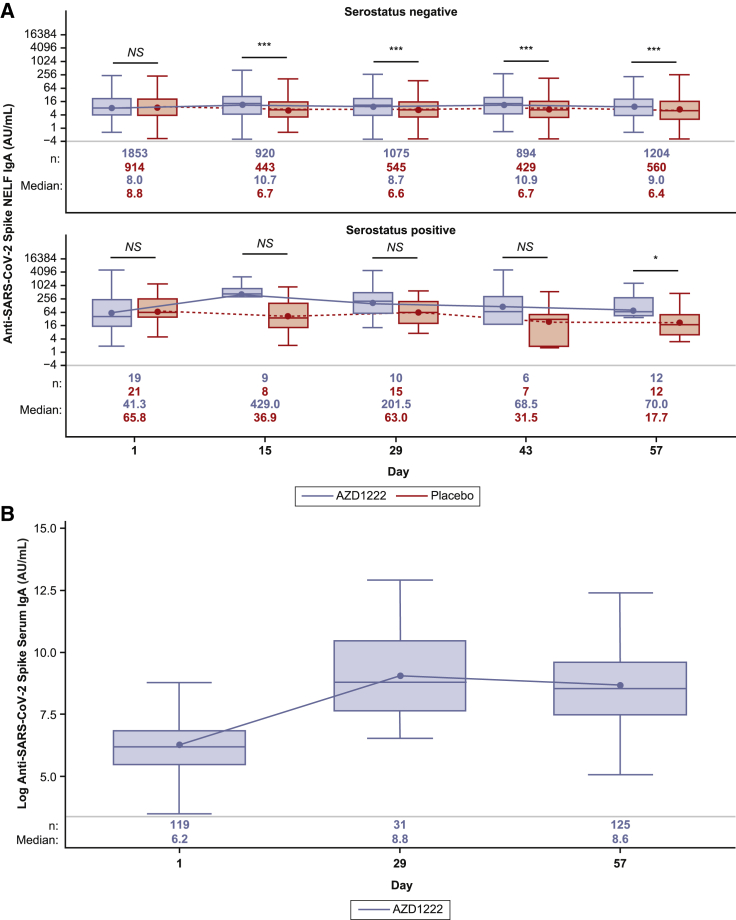
Figure 2.
Quantification of anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike IgA in NELF and serum from immuno-genicity substudy participants following AZD1222 vaccination or placebo
(A) Boxplots illustrating anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike IgA titers observed in NELF following AZD1222 vaccination or placebo according to participant baseline SARS-CoV-2 serostatus, as determined by the presence of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antibodies. To provide comprehensive information about the durability of immunogenicity after vaccination, data were censored in AZD1222 study participants at the time of non-study COVID-19 vaccination and for placebo participants at the earlier of the time of non-study COVID-19 vaccination or unblinding, whichever occurred first.
(B) Post hoc analysis of IgA titers observed in serum of baseline-seronegative participants following AZD1222 vaccination. The x axis denotes days since the first AZD1222 or placebo dose. Day 1 and day 29 samples were obtained prior to administration of AZD1222 or placebo. The box denotes IQR, the horizontal line in the box denotes median, and the marker in the box is the GMT. Any points more than 1.5 × IQR from the box were considered outliers and are not displayed. The whiskers that extend from the box indicate the minimum and maximum after removing the outliers. Boxplots were created using the log-normal distribution. Data were censored in participants at the time of non-study COVID-19 vaccination during this post hoc analysis of baseline-seronegative AZD1222 vaccinees. Participants who tested positive for the presence of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antibodies at any time after day 1 were excluded from this analysis.
Statistical evidence between groups was determined by post hoc two-tailed Mann-Whitney tests. NS, p > 0.05; ∗p ≤ 0.05; ∗∗p ≤ 0.01; ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001.