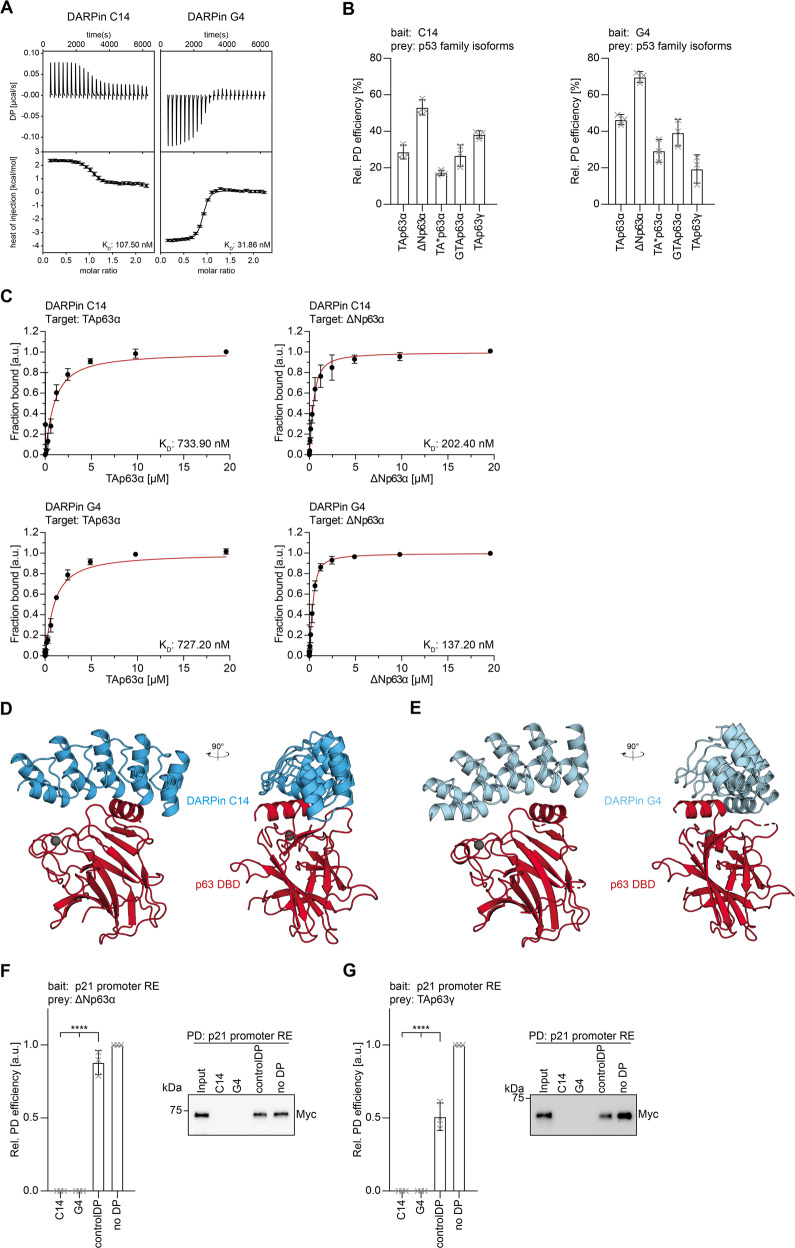
Fig. 1. Characterization of DBD-specific DARPins.
A ITC measurements of the DARPins C14 and G4 interacting with the DBD of p63. In each plot the top diagram displays the raw measurements and the bottom diagram shows the integrated heat per titration step. KD values are given for each DARPin. B Pulldown experiments with different in-vitro translated p63 isoforms and immobilized DARPins, showing that both DARPins bind all isoforms. The pulldown efficiency relative to the whole protein expression is displayed on the y-axis (n = 3). C Fluorescence anisotropy measurements of Alexa 488 labeled DARPins with purified full-length TAp63α and ΔNp63α isoforms confirming that both DARPins bind all dimeric and tetrameric isoforms. The KD values are provided for each experiment. D Crystal structure of the DARPin C14 in complex with the p63 DBD shown in two different orientations rotated by 90°. E Crystal structure of the DARPin G4 in complex with the p63 DBD shown in two different orientations rotated by 90°. F, G DNA-pulldown experiments with ΔNp63α (F), TAp63γ (G), and an immobilized DNA oligomer containing the 20 bp binding site of the human p21 promoter. Pre-incubation of the p63 isoforms with DARPin C14 or DARPin G4 inhibits interaction with the DNA oligomer while a control DARPin does not prevent binding. Corresponding western blot results are shown on the right. The relative pulldown efficiency normalized to no DARPin is shown on the y axis (n = 3). The bar diagram shows the mean values and error bars show the corresponding SD of three biological replicates. Statistical significance was assessed by ordinary one-way ANOVA.