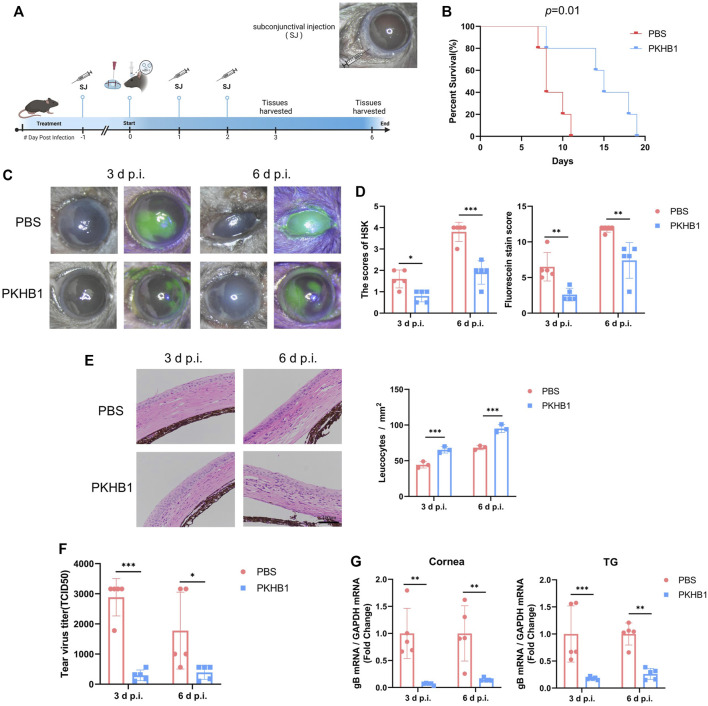
FIGURE 2.
Subconjunctival injection of PKHB1 peptide inhibited HSV-1 replication and alleviated HSK lesions. (A) Drug delivery procedure and photograph of mice eyes after subconjunctival injection. (B) PKHB1-treated mice had longer survival rates. Photographs (C) and scores (D) of corneal lesions and sodium fluorescein staining in mice (n = 3–5). (E) HE staining of mouse corneal sections and quantifying leukocytes infiltration. (F) Virus titers of mouse tear swabs were calculated based on the Reed-Muench method. Virus titers of the PKHB1-treated mice were significantly lower (n = 5). (G) qRT-PCR was performed to detect the expression levels of HSV-1 gB in mice corneas and TGs at 3 d p.i. and 6 d p.i. (n = 5), which were significantly reduced in the PKHB1-treated mice. GAPDH was used as an internal reference. Data were presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001)