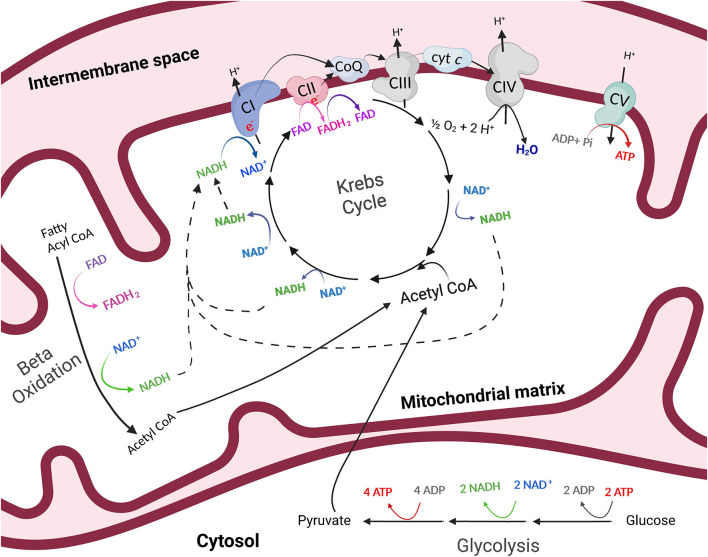
Figure 1.
The process of energy production outside of (glycolysis) and within (oxidative phosphorylation) the mitochondria. Through anaerobic glycolysis, glucose is metabolized in the cytosol of the cell to pyruvate. Pyruvate may then be transported into the mitochondria where it is oxidized to acetyl CoA, which enters the Krebs cycle in the mitochondrial matrix. The byproducts of the Krebs cycle, NADH and FADH2, provide high-energy electrons to the electron transfer system which resides in the inner mitochondrial membrane. As electrons are transferred, protons are pumped into the intermembrane space of the mitochondria and a proton gradient is generated. Protons then flow through ATP synthase, or complex V (CV) of the electron transfer system, following the chemical gradient to combine with adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi), creating ATP. This process is referred to as oxidative phosphorylation. Created with Biorender.com.