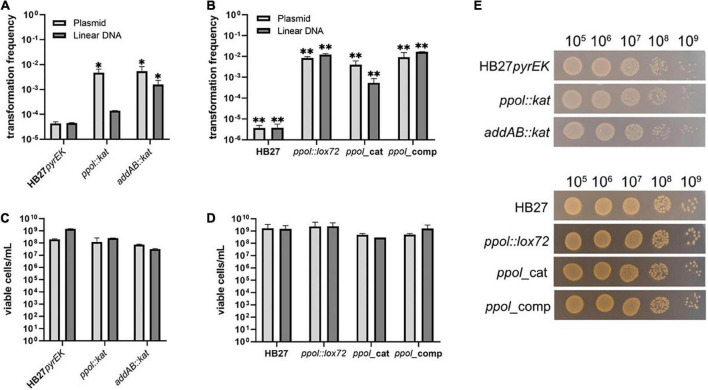
FIGURE 2.
Transformation efficiency of Thermus thermophilus mutants. (A) Hundred nanogram of a replicative plasmid (pMotH1103A) or an homologous-recombination integrative linear DNA fragment conferring resistance to Hyg (pyrEH), were used to transform Tth HB27pyrEK control strain and ppol:kat and addAB:kat insertion mutant. (B) Hundred nanogram of a replicative plasmid (pMotK1103A) or an homologous-recombination integrative linear DNA fragment (pyrEK) conferring resistance to Kn, were used to transform Tth HB27 cells and its derivatives ppol:lox72, ppol_cat, ppol_comp, addAB:lox72, and addAB_ppol mutants. (C) Viable cells per mL of the kat-marked transformed strains in Kn plates. (D) Viable cells per mL of the markerless transformed strains in TB plates. (E) Serial dilutions of transformed cells of the indicated strains plated on Kn (upper panel) or non-selective plates (lower panel) and incubated for 48 h at 65°C. Transformation is represented as the number of colonies on selection plates at 65°C, relative to the number of viable colonies on non-selective plates. Transformation frequencies were calculated as an average of at least five biological replicates. Error bars correspond to the standard deviation of the means. Asterisks indicate statistically different values observed in mutant strains compared to those in the corresponding control strains (*P-value <0.005 and **P-value <0.0001).