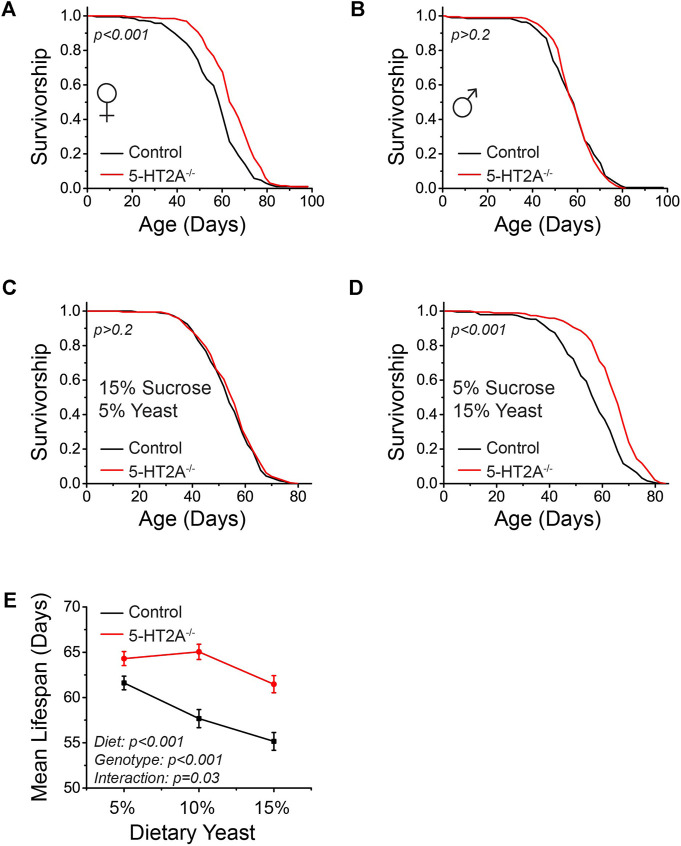
FIGURE 1.
5-HT2A interacts with protein levels to modulate lifespan. (A) Female 5-HT2A −/− mutants are long-lived relative to white-eyed Canton-S (w-; CS) controls on a standard laboratory diet consisting of 10% sucrose and 10% yeast (n = 193 and 188, log-rank analysis p < 0.001). (B) Male 5-HT2A −/− mutants are not long-lived relative to w-; CS controls on a 10% sucrose and 10% yeast diet (n = 194 and 192, log-rank analysis p = 0.71). (C) 5-HT2A −/− mutant females do not show a lifespan extension on a 15% sucrose/5% yeast diet (n = 193 and 185, log-rank analysis p = 0.4). (D) 5-HT2A −/− mutant females are long-lived on a 5% sucrose/15% yeast diet (n = 195 and 193, log-rank analysis p < 0.001). (E) The mean lifespan of w-; CS control females decreases significantly as dietary protein increases (n = 187–195, One-way ANOVA Diet: p < 0.001), and dietary protein slightly significantly affects lifespan in 5-HT2A −/− mutant females (n = 187–195, One-way ANOVA Diet: p = 0.01). The 5-HT2A −/− mutant lifespan is significantly different from that of controls across diets containing 5%–15% yeast (n = 187–195, ANCOVA Diet: p < 0.001 Genotype: p < 0.001 Interaction: p = 0.03). Censored observations were ignored for the analysis of mean longevity.