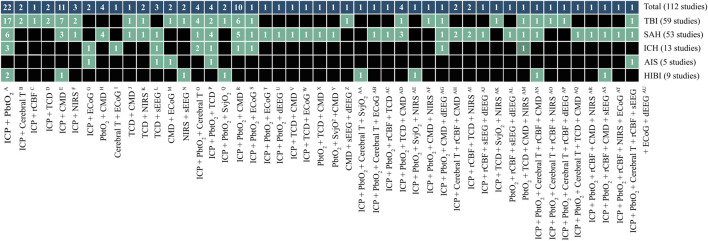
FIGURE 3.
Unique cerebral multimodality monitoring combinations. The 47 unique combinations of MMM are shown. The first upper row shows the total number of studies per combination. The second to the sixth row shows the number of studies per acute brain injury: TBI, SAH, ICH, AIS, and HIBI. Each box describes the number of studies. The boxes in black do not include a monitoring combination for a particular disease. The references of the studies are added to Supplementary Tables S5A–D. The reference numbers per unique combination are: A (11,14,24,33,43,46,47,48,49,53, 69,71,87,90,91,94,97, 104,105,106,107,110); B (51,55); C (4); D (76,31); E (9,38,45,61,62,63,66,67,77,82,101); F (32,37,73); G (8,60); H (17,70,95,98); I (21); J (78); K (6,74); L (23,57,58); M(10,20); N (68,79); O (30,40,42,100); p (83,86,93,96); Q (35,44); R (1,3,13,19,34,52,56,59,89,102); S (2); T (27); U (29); V (112); W (64); X (99); Y (5); Z (15); AA (111); AB (16); AC (103); AD (80,92,108,109); AE (81); AF (41); AG (50); AH (12,39); AI (75,88); AJ (18); AK (84); AL (22); AM(72); AN (36); AO (7); AP (26); AQ (85); AR (54); AS (28); AT (65); AU (25). Note: the sum of studies for the individual diseases not count towards the total number of studies because a study can include patients with different diseases. AIS, acute ischemic stroke; Cerebral T, cerebral temperature; CMD, cerebral microdialysis; dEEG, depth electroencephalography; ECoG, electrocorticography; HIBI, hypoxic-ischemic brain injury following cardiac arrest; ICH, intracerebral hemorrhage; ICP, intracranial pressure; NIRS, near-infrared spectroscopy; PbtO2, partial pressure of brain tissue oxygenation; rCBF, regional cerebral blood flow; SAH, subarachnoid hemorrhage; sEEG, surface electroencephalography; SvjO2, jugular bulb venous oximetry; TBI, traumatic brain injury; TCD, transcranial Doppler.