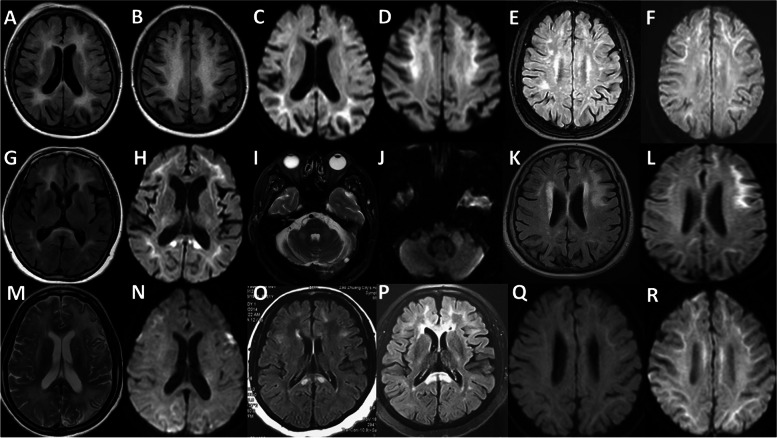
Fig. 1.
A-D F/64, widespread leukoencephalopathy with frontal lobe predominance and corticomedullary junction DWI high intensity, involving corpus callosum and external capsule. E–F F/55, patchy frontal lobe leukoencephalopathy with corticomedullary junction DWI high intensity. G-H F/59, frontal lobe and external capsule DWI high intensity with splenium of corpus callosum lesions. I-J M/61, symmetrical lesions on brachium pontis and DWI high intensity. K-L F/54, asymmetrical distribution of frontal lobe leukoencephalopathy. M–N F/45, widespread leukoencephalopathy with grey matter involvement, left predominance. O-P F/54, progression of leukoencephalopathy after 4 years follow-up. Q-R F/51, extensive increase of corticomedullary junction DWI high signal after 2 months follow up, while no change in FLAIR sequence. (FLAIR: A, B, E, G, K, O, P; T2-weighted: I, M; DWI: C, D, F, H, J, L, N, Q, R)