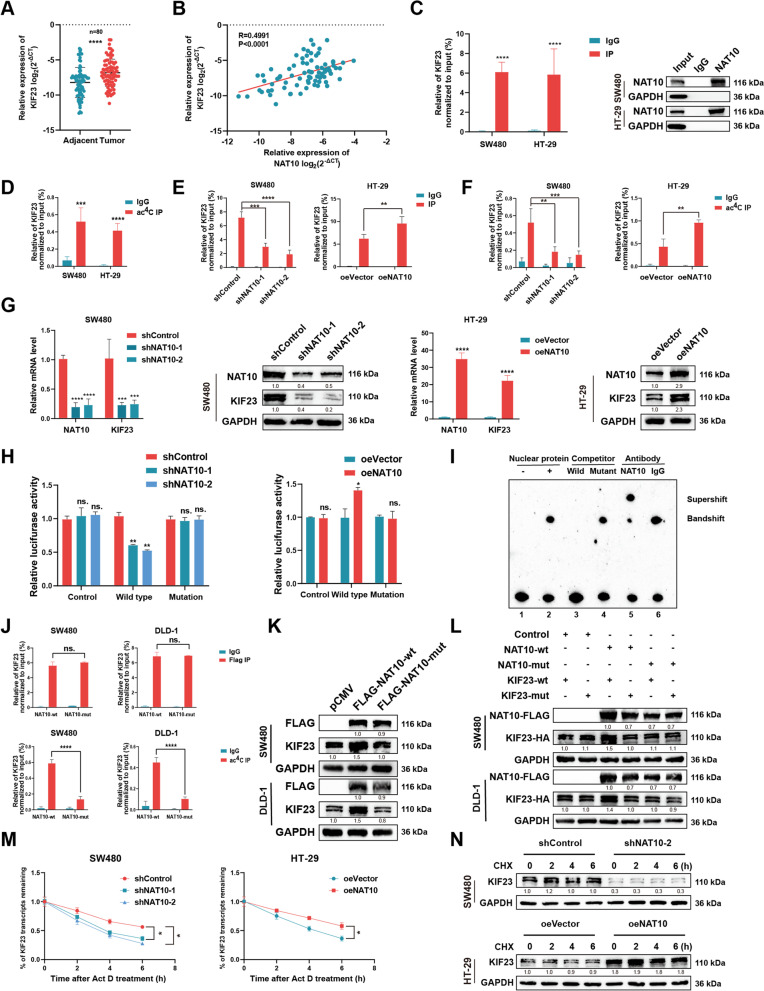
Fig. 5.
NAT10 stimulates the expression of KIF23 through ac4C modification. A The mRNA level of KIF23 detected by qRT-PCR in 80 CRC tissues and matched adjacent tissues. B Correlation analysis between the mRNA levels of NAT10 and KIF23. C NAT10 RIP followed by qPCR in SW480 and HT-29 cells. D acRIP followed by qPCR in SW480 and HT-29 cells. E The interaction between NAT10 and KIF23 mRNA was analyzed by RIP-qPCR assay in CRC cells with NAT10 knockdown or overexpression. F The relative levels of ac4C in KIF23 were tested by acRIP-qPCR in CRC cells with NAT10 knockdown or overexpression. G Relative RNA and protein level of KIF23 in CRC cells upon NAT10 knockdown or overexpression. H The luciferase activity for the reporter containing the NAT10-binding region or mutant upon NAT10 knockdown or overexpression. I REMSA assays to detect the combination of NAT10 and the ac4C motif on KIF23 mRNA. J RIP and acRIP followed by qPCR upon the transfection of NAT10-wt or NAT10-mut in CRC cells. K The expression of KIF23 upon overexpression of Flag-tagged NAT10 wide-type or its mutant, as determined by WB in SW480 and DLD-1 cells. L The expression of KIF23 in SW480 or DLD-1 cells co-transfected with empty vector, wild-type or mutant Flag-tagged NAT10, and wild-type or mutant HA-tagged KIF23. M The mRNA stability was detected by qRT-PCR in SW480 and HT-29 cells with the addition of actinomycin D (5 μg/mL). N The protein expression of KIF23 with the treatment of CHX (100 μg/mL) in CRC cells upon NAT10 knockdown or overexpression. Data are shown as mean ± SD of three independent experiments, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, ns. not significant