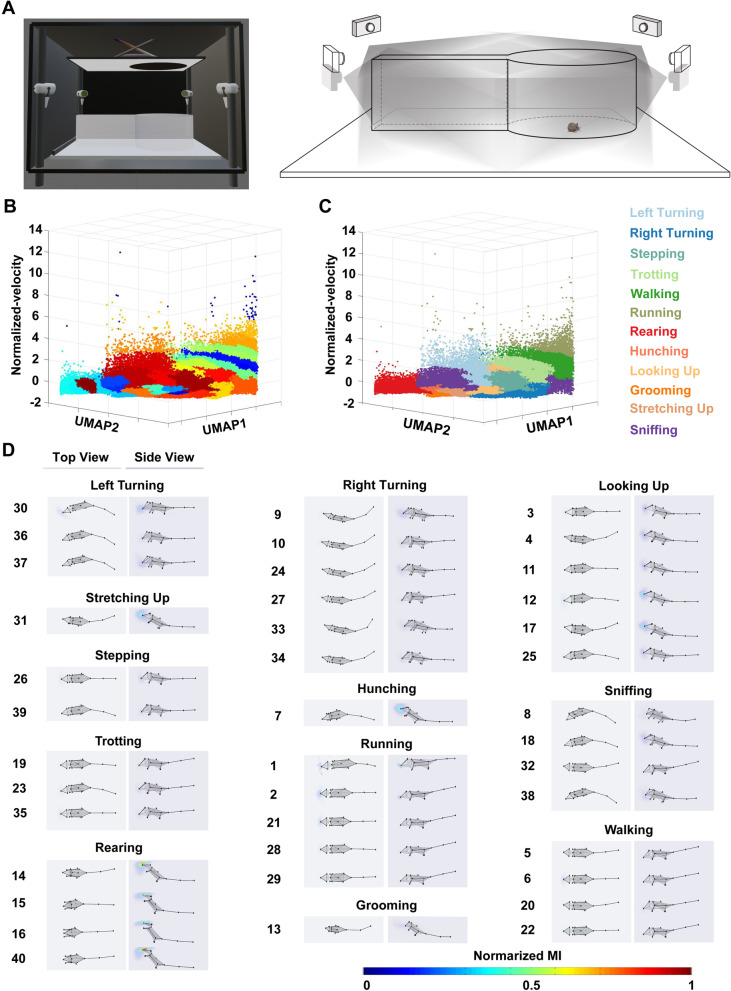
Fig. 2.
The 3D-motion multi-layered framework adapted for the visually-evoked defensive behavior paradigm. A Schematic showing the experimental setup (left) and schematic diagram of the behavioral recording arena with four synchronized cameras (right). B Spatiotemporal feature space of behavioral components with unsupervised learning. C Spatiotemporal feature space of behavioral components. D Average skeleton positions from all frames within each movement phenotype. Skeletons are shown with solid lines and calculated by averaging poses of body parts over time. The heatmaps overlaid on the average noses position correspond to the normalized moving intensity (MI) of each movement phenotype