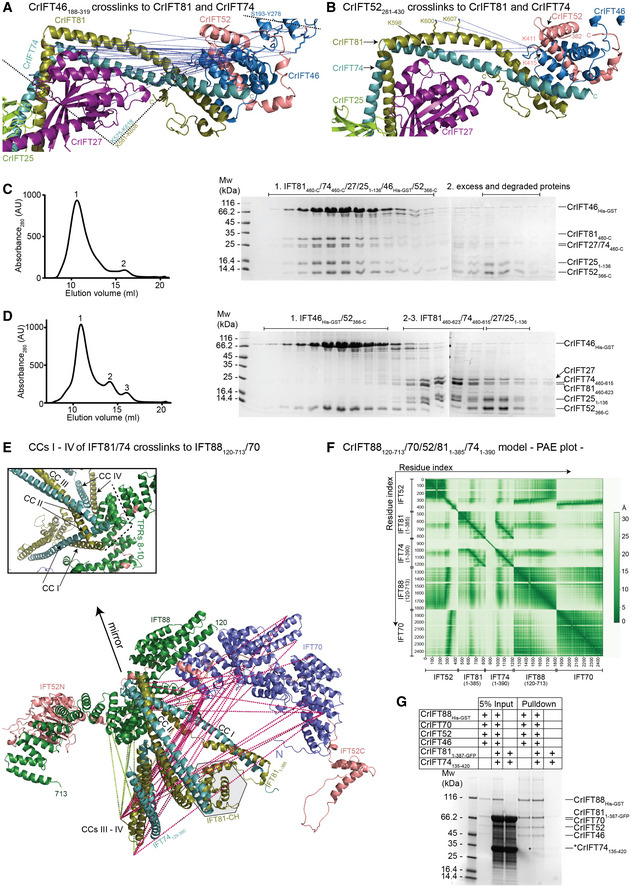
Figure 4. IFT81/74 has two separate binding sites on IFT88/70/52/46.
-
AThe blue dotted lines indicate the IFT46 cross‐links to the C‐termini of IFT81 and IFT74. These cross‐links map to a 43 residue stretch from K575 to K618 in IFT81 and a 27 residue stretch in IFT74 bordered by K581 and K608. An additional cross‐linking pair was identified between IFT46 and IFT27.
-
BK411 and K415 of IFT52 cross‐link to K598, K600, and K607 of IFT81. These cross‐links are labeled as in panel (A).
-
C, DThe C‐terminal domains of IFT52 and IFT46 co‐purify with the IFT81460‐C/74460‐C/27/251–136 protein complex (C) but not with a protein complex that is missing residues 623‐C of IFT81 and 615‐C of IFT74 (D). The SEC fractions indicated on the right with 1–3 were analyzed by SDS‐PAGE and stained with Coomassie to evaluate the protein composition.
-
EIFT811–385/74128–390 cross‐linking network with IFT88, IFT70, and IFT52 labeled on the AF predicted model of Chlamydomonas IFT88120–713/70/52/811–385/741–390. The N‐terminal 128 amino acids of IFT74 are predicted to be unstructured and omitted from the figure for clarity. The box shows a zoom‐in on the IFT81/74/88 interaction interface.
-
FThe predicted alignment error plot of the Chlamydomonas IFT88120–713/70/52/811–385/741–390 complex shown in panel (E).
-
GCoomassie stained SDS PAGE gel of a GST‐pull down using the CrIFT88His‐GST/70/521–430/46 complex immobilized on GST beads as bait and the CrIFT811–387‐GFP/74135–420 complex used as prey. The band highlighted by an * corresponds to pulled down CrIFT74135–420. CrIFT811–387‐GFP runs on top of IFT70 and is not visible in the pull down.
