Figure 2.
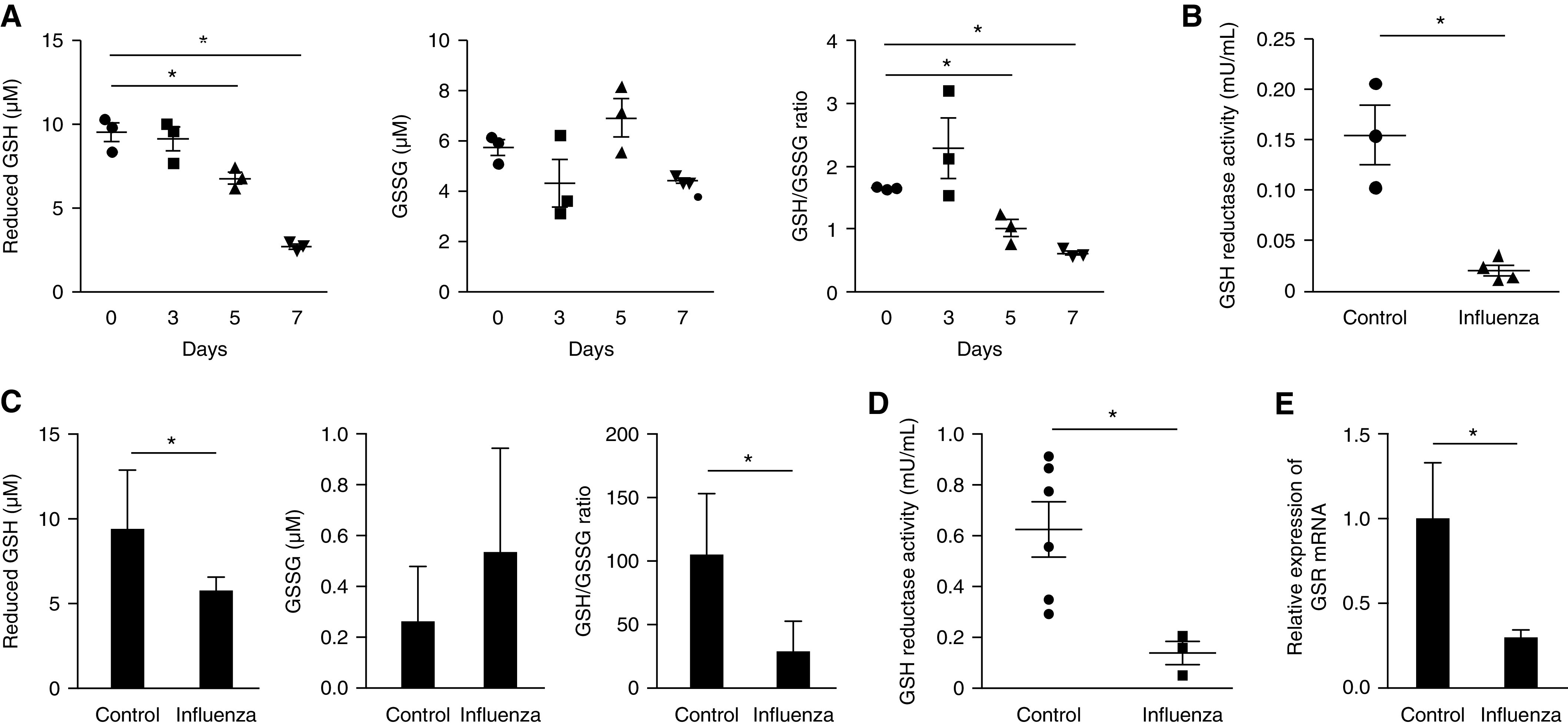
Influenza infection induces alteration of glutathione metabolism in vivo and in vitro. (A) Total, reduced, and oxidized forms of glutathione and the ratio of reduced and oxidized glutathione measured in lung tissue lysate of influenza-infected mice (125 PFU, n = 3 mice per group). (B) Glutathione reductase activity in murine lung 7 days after influenza infection. (C) Total, reduced, and oxidized forms of glutathione and the ratio of reduced and oxidized glutathione measured in Beas2B cells after treatment with influenza (1.25 × 104 PFU) for 48 hours. (D) Glutathione reductase activity and (E) gene expression of glutathione reductase in Beas2B cells 48 hours after influenza infection. Data are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 by ANOVA. Results are representative of three or more independent experiments.
