Figure 7.
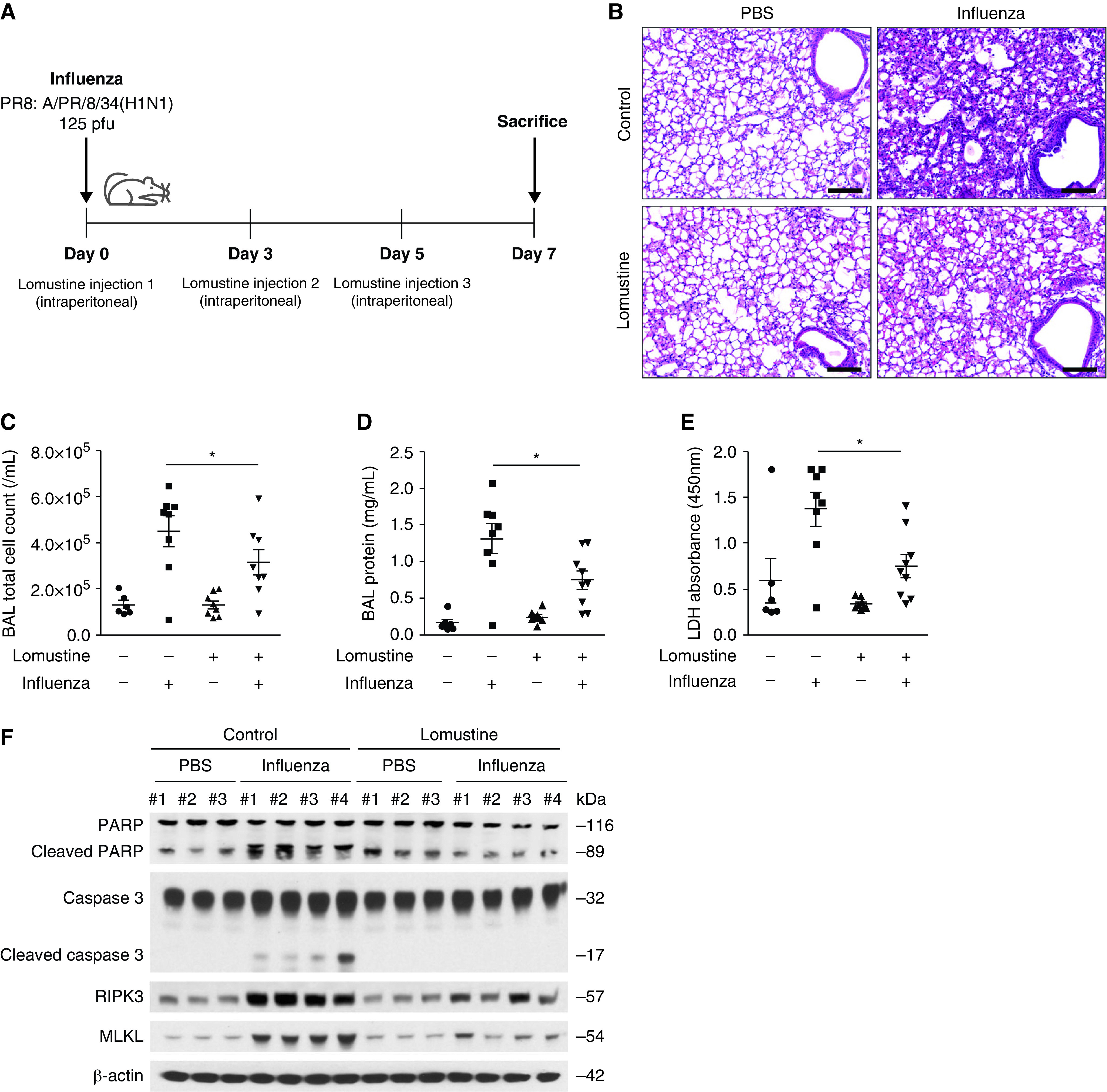
Pharmacologic inhibition of glutathione reductase reduced airway inflammation, lung injury, and cell death. (A) Experimental layout of influenza-induced lung injury in lomustine-treated mice (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection on Days 0, 3, and 5). Lung tissue and BAL fluids were obtained on Day 7. (B) Representative lung sections of influenza-infected mice after lomustine treatment. Stained with hematoxylin and eosin staining. Scale bars, 200 μm. (C) BAL cell count, (D) the protein concentration in BAL fluid, and (E) lactate dehydrogenase cytotoxicity in influenza-infected mice after lomustine treatment (n = 69 mice/group). Data are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 by ANOVA. (F) Immunoblot analysis for PARP, cleaved PARP, caspase 3, cleaved caspase 3, RIPK3, and MLKL in influenza-infected lung after lomustine treatment. Results are representative of two independent experiments.
