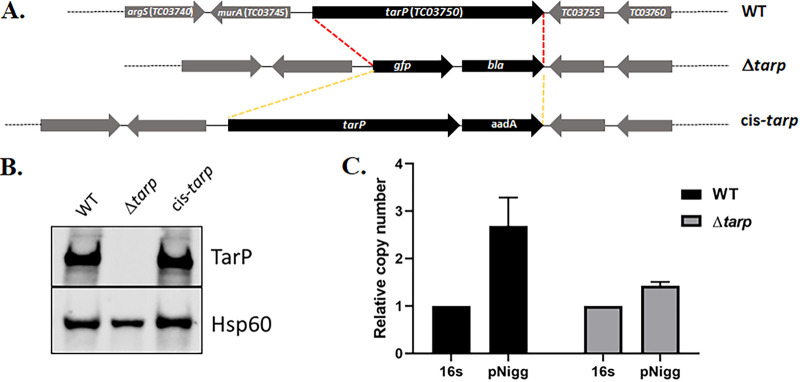
FIG 4.
Generation of the tarP-null mutant and cis-complemented strain in C. muridarum. (A) Schematic representation of the strategy employed in deletion of the entire tarP gene from the chlamydial genome and generation of a cis-complemented strain by allelic replacement. (B) Western blot analysis with anti-Tarp polyclonal antiserum, demonstrating the absence of the tarP gene in C. muridarum-infected cell cultures compared the WT or cis-tarp-complemented strains. Probing with genus-specific anti-Hsp60 monoclonal antibody was included as a loading control. (C) qPCR analysis of Δtarp- and WT C. muridarum-infected cells showing the presence of the native plasmid in both chlamydial strains. The copy number of genes pgp7-pgp8 is presented relative to a 16S rRNA region.