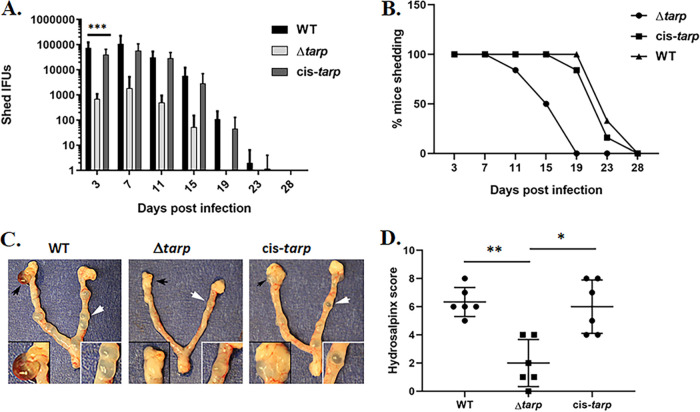
FIG 6.
Attenuation of Δtarp C. muridarum in a mouse infection model. Groups of 6 mice were challenged intravaginally with equal infectious units of WT, Δtarp, or cis-tarp C. muridarum, and the shed infectious particles were enumerated from days 3 to 28. Average progeny numbers shed (A) and percentage of mice actively shedding chlamydiae (B) at different days postinfection. Significance was determined by two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) (***, P < 0.0004). Reproductive tracts were excised on day 60 postinfection and assessed for gross pathology. (C) Representative images are shown from each group, and areas of hydrosalpinx and tubal dilation are highlighted in insets (black or white arrows, respectively). (D) Plot of hydrosalpinx severity score data for each mouse. A Wilcoxon rank-sum test was performed to address significance (*, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.002).