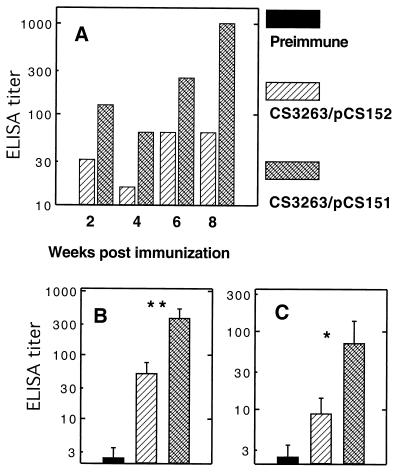
FIG. 4.
987P fimbria-specific mucosal IgA responses in pooled stools (A), gut washes (B), and bile (C). BALB/c mice were immunized orally with two doses (26-day interval) of serovar Typhimurium CS3263/pCS152 (fasD) expressing fimbrial antigen in the periplasm (hatched bars) or serovar Typhimurium CS3263/pCS151 expressing 987P fimbriae on the surface (crossed bars). The fecal pellets were collected biweekly. The gut washes and bile were collected before immunization and at 6 to 8 weeks after immunization. The samples collected before immunization (solid bars) were used as a control. The IgA in the stools were measured from pooled fecal pellets. IgA levels in gut washes and bile were measured individually, and error bars represent standard deviations of the values for eight mice. No antibodies were detected in fecal pellets from preimmunized mice. IgA titers elicited by serovar Typhimurium CS3263/pCS151 in the gut washes and bile were significantly higher than the titers induced by serovar Typhimurium CS3263/pCS152 (∗, P < 0.05; ∗∗, P < 0.01).