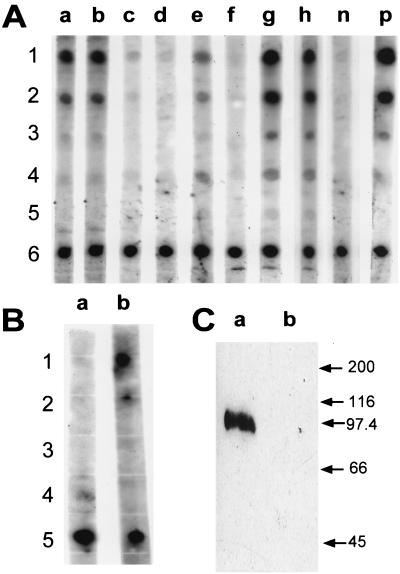
FIG. 8.
Dot blots and Western blot demonstrating systemic and mucosal antibody response to the TGEV C or A epitope. (A) TGEV C epitope-specific serum IgG were detected by dot blot assay after oral immunization of four different BALB/c mice with serovar Typhimurium χ4550/pCS154 (lanes a to d). TGEV C and A epitope-specific serum IgG were detected after oral immunization of four different BALB/c mice with serovar Typhimurium χ4550/pCS155 (lanes e to h). Rabbit anti-wild-type 987P serum was used as negative control (lane n), and rabbit anti-chimeric 987P-TGEV C serum was used as positive control (lane p). The sera from the immunized mice were diluted 1:100. The antigen in rows 1, 2, and 3 was TGEV C peptide at 2, 0.4, and 0.1 μg per spot, respectively. The antigen in rows 4 and 5 was TGEV A peptide at 2 and 0.4 μg per spot, respectively. The antigen in row 6 was purified wild-type 987P fimbriae at 0.1 μg per spot. (B) TGEV C epitope-specific IgA was detected in pooled fecal pellets (diluted 1:10) by a dot blot after oral immunization of BALB/c mice with serovar Typhimurium χ4550/pCS155 (lane b) but not after oral immunization with serovar Typhimurium χ4550/pCS154 (lane a). The antigen in rows 1 and 2 was TGEV C peptide at 2 and 0.4 μg per spot, respectively. The antigen in rows 3 and 4 was TGEV A peptide at 2 and 0.4 μg per spot, respectively. The antigen in row 5 was purified wild-type 987P fimbriae at 0.1 μg per spot. (C) Western blot with serum from one representative mouse immunized with serovar Typhimurium χ4550/pCS155. The anti-TGEV epitope antibody can recognize the epitope in the context of the TGEV S protein R2-2 expressed by recombinant baculovirus (lane a). Sf9 is the baculovirus mock protein used as negative control (lane b). Molecular masses (in kilodaltons) of standard proteins are shown on the right.