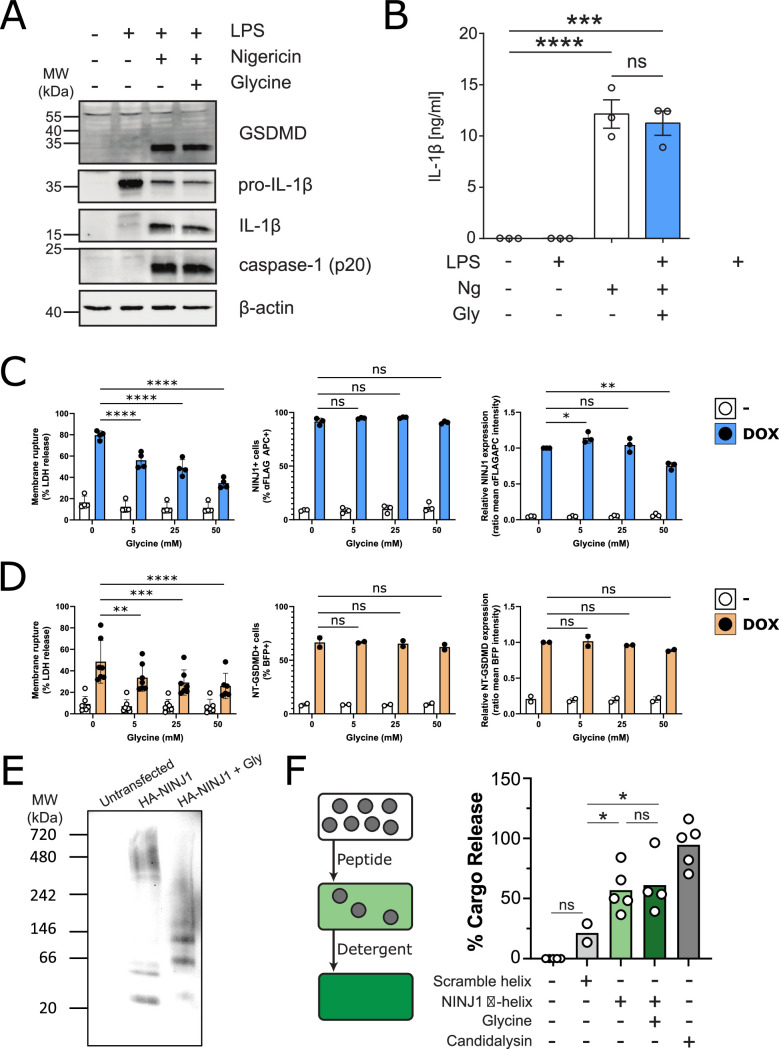
Figure 5. Glycine inhibits NINJ1 clustering but not upstream pyroptosis signaling to confer cytoprotection.
(A–B) Wildtype immortalized bone marrow-derived macrophage (iBMDM) was primed with 1 μg/mL LPS for 4 hr or left unprimed before stimulation of primed cells with 20 μM nigericin for 2 hr in the presence or absence of 5 mM glycine. (A) Processing of GSDMD, caspase-1, and IL-1β was assessed by western blot. (B) Release of IL-1β into the cell culture supernatant was quantified by ELISA. ELISA results show mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Western blots are representative of three independent experiments. ***p<0.001 and ****p<0.0001 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison correction. (C–D) Glycine dose-dependently inhibits plasma membrane rupture in mouse macrophages overexpressing NINJ1 or the N-terminal fragment of GSDMD. iBMDMs with doxycycline-inducible expression of FLAG-tagged NINJ1 (C) or the N-terminal fragment of GSDMD fused to BFP(blue fluorescent protein) (D) were incubated with 2 µg/mL doxycycline and increasing concentrations of glycine for 12 hr or 8 hr, respectively, before analyses of cell rupture (LDH release) and protein expression. Left: LDH release in supernatants relative to full lysis controls. Middle: frequencies of NINJ1-FLAG-positive or GSDMD-NT-BFP-positive cells. Right: surface expression of NINJ1-FLAG or GSDMD-NT-BFP by mean fluorescence intensity. * p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, and ****p<0.0001 by two-sided ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison correction. (E) HeLa cells were transiently transfected with HA-tagged mouse NINJ1 in the presence or absence of glycine (5 mM). Native-PAGE analysis of ectopically expressed NINJ1 demonstrates a shift to high molecular weight aggregate, which is abrogated by glycine treatment. (F) Large unilamellar vesicles (LUVs; gray circles) were made containing 25 mM carboxyfluorescein (CF) at which the CF fluorescence self-quenches. NINJ1 α-helix peptide (corresponding to amino acids 40–69 of human NINJ1) is added to the LUV suspension. Ruptured LUV release CF, which no longer self-quenches. The resulting increase in fluorescence is monitored using a spectrofluorometer. Detergent is added to rupture all remaining liposomes to capture the maximum attainable fluorescence. LUV rupture by N-terminus NINJ1 α-helix without and with glycine (50 mM), scrambled NINJ1 α-helix peptide, or the cytolytic yeast peptide candidalysin compared to vehicle. Glycine does not prevent LUV rupture by the N-terminal NINJ1 α-helix. * p<0.05 by ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison correction.