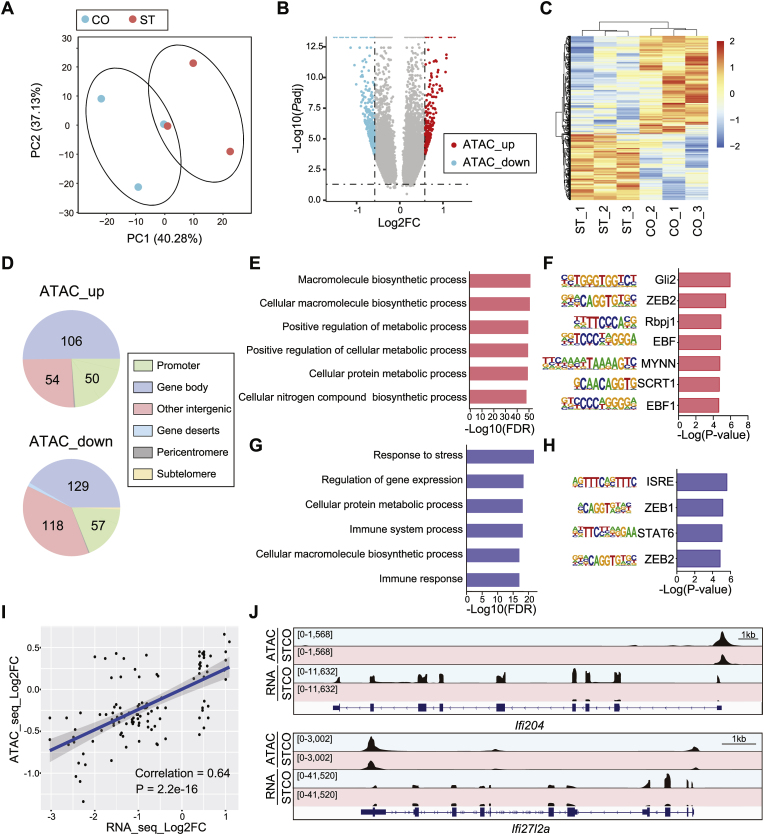
Fig. 5.
Microglia-specific alterations of chromatin accessibility after chronic stress. (A) PCA plot of ATAC-seq using isolated microglia from mice exposed to chronic stress (ST) and controls (CO). N = 3/group. (B) The volcano plot and (C) clustered heatmap show differential ATAC-seq signals in microglia after chronic stress (ST v.s. CO). Red dot, up-regulated loci (ATAC_up); blue dot, down-regulated loci (ATAC_down); gray dot, non-significant loci. FDR <0.05. (D) Genome annotations for up-and down-regulated ATAC-seq loci. (E, G) GO analysis for genes associated with (E) up- and (G) down-regulated loci, defined as “promoter + gene body”. (F, H) Homer de novo motif prediction for (F) up- and (H) down-regulated loci. (I) Pearson's correlation test for RNA-seq and ATAC-seq signal at differential gene loci. (J) IGV map tracks show ATAC-seq and RNA-seq signals at Ifi204 and Ifi27l2a loci. Notice decreased ATAC-seq (gene promoter) and RNA-seq (coding sequence) signal in the ST compared to CO. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)