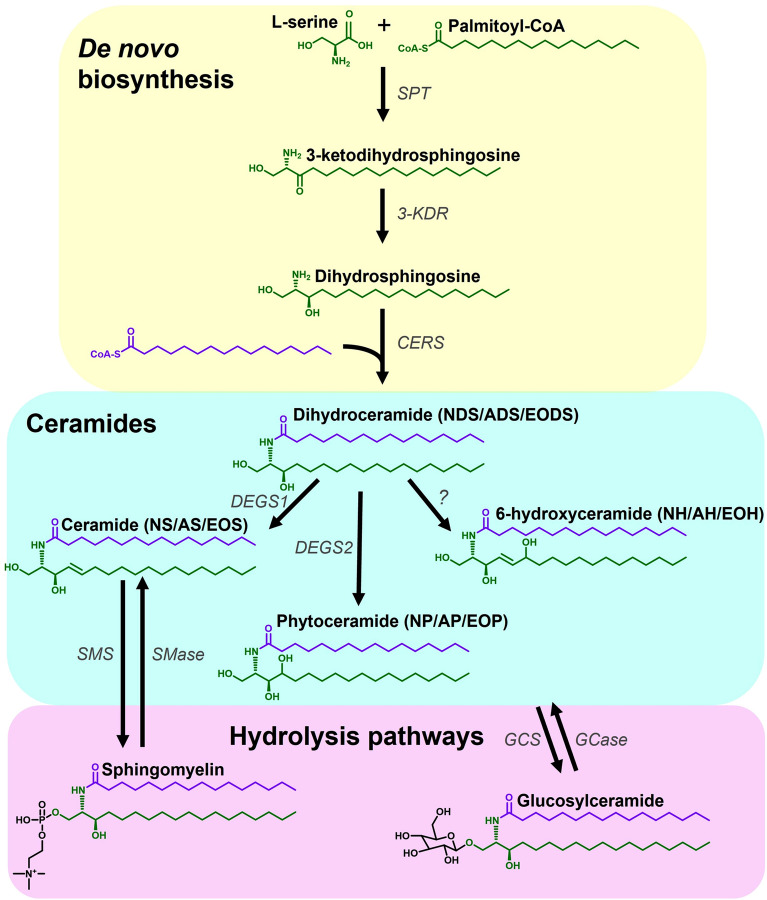
Figure 1.
Summary diagram showing parts of the ceramide synthesis pathway. Ceramides are synthesised de novo via the combination of a sphingoid base, generated by the condensation of l-serine and an acyl-CoA, with an acyl chain, via the action of ceramide synthase enzymes. The dihydroceramide formed can be converted to different ceramide classes via the action of dihydroceramide desaturases. Ceramides can be reversibly converted to sphingomyelins (CER[NS/AS]) or glucosylceramides via the main hydrolysis pathways. Alterations in the de novo and hydrolysis pathways can alter the levels of ceramides measured. 3-KDR 3-ketodihydrosphingosine reductase, AH alpha-hydroxyceramide with 6-hydroxysphingone base, AP alpha-hydroxyceramide with phytosphingosine base, AS alpha-hydroxyceramide with sphingosine base, CERS ceramide synthases, DEGS1 dihydroceramide desaturase 1, DEGS2 dihydroceramide desaturase 2, EODS ester-linked omega hydroxy dihydroceramide, EOH ester-linked omega hydroxy 6-hydroxyceramide, EOP ester-linked omega hydroxy phytoceramide, EOS ester-linked omega hydroxyceramide, GCase glucosylceramidase, GCS glucosylceramide synthase, NH non-hydroxyceramide with 6-hydroxysphingone base, NP non-hydroxyceramide with phytosphingosine base, NS non-hydroxyceramide with sphingosine base, SMase sphingomyelinase, SMS sphingomyelin synthase, SPT serine palmitoyltransferase, ? as-yet unidentified desaturase enzyme.