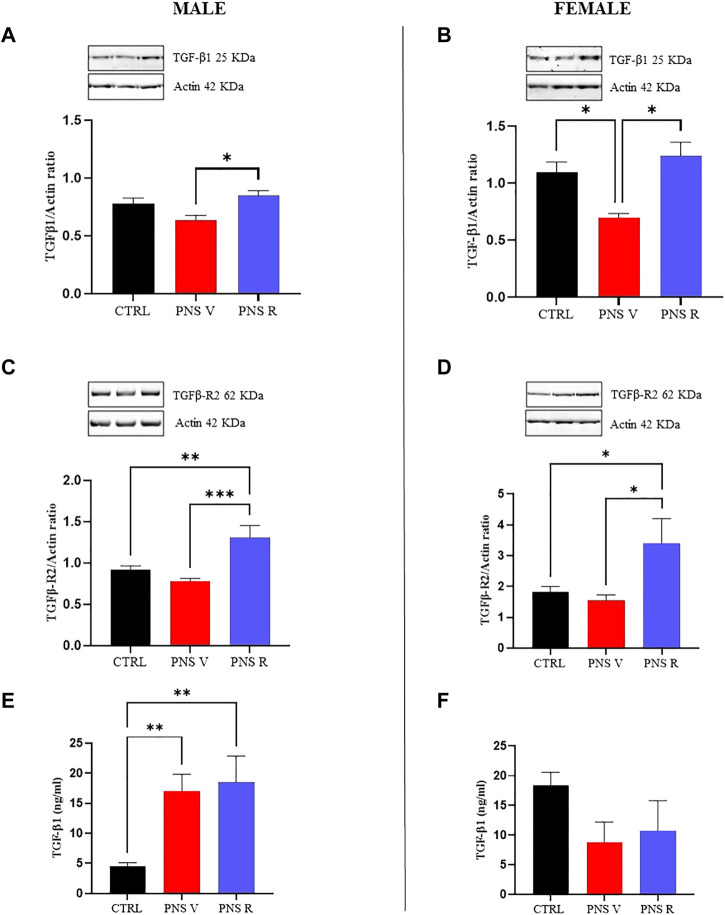
FIGURE 4.
Role of TGF-β1 pathway in the mechanisms of vulnerability and resilience to PNS exposure. Effects induced by PNS exposure on TGF-β1 levels and of its receptor TGFβ-R2 in total protein extracts from hippocampus of CTRL and PNS rats evaluated by Western Blot analysis. (A) Representative immunoblot and histogram of TGF-β1 (44 kDa) in CTRL and PNS male adolescent rats (*p < 0.05 vs. PNS V). (B) Representative immunoblot and histogram of TGF-β1 (44 kDa) in CTRL and PNS female adolescent rats (*p < 0.05 vs. CTRL; *p < 0.05 vs. PNS V). (C) Representative immunoblot and histogram of TGFβ-R2 (65 kDa) in CTRL and PNS male adolescent rats (**p < 0.01 vs. CTRL; ***p < 0.001 vs. PNS V). (D) Representative immunoblot and histogram of TGFβ-R2 (65 kDa) in CTRL and PNS female adolescent rats (*p < 0.05 vs. CTRL; *p < 0.05 vs. PNS V). TGF-β1 and TGFβ-R2 densitometric values were normalized against actin used as internal control. Plasmatic levels of TGF-β1 (ng/ml) in male (E) (**p < 0.01 vs. CTRL) and female (F). All data are shown as mean ± SEM of CTRL male n = 10; PNS V male n = 9; PNS R male n = 5; CTRL female n = 10; PNS V female n = 5; PNS R female n = 4.