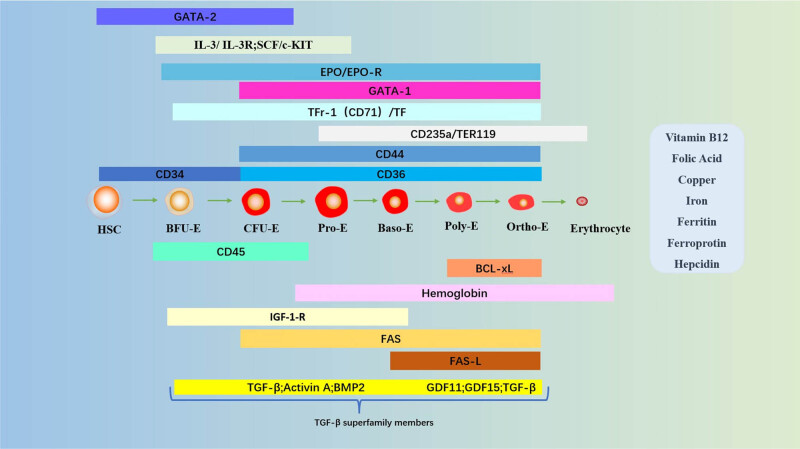
Figure 4.
The main pathways and molecules involved in regulating erythropoiesis. The different stages are shown: HSC, BFU-E, CFU-E, Pro-E, Baso-E, Poly-E, Ortho-E, and erythrocytes. Molecules involved: zinc finger factors that bind GATA sequences (GATA-1, GATA-2); IL-3; IL-3-R; SCF; c-Kit; EPO; EPO-R; Ter-119, glycophorin A-associated protein; CD235a, glycophorin A; CD44, cell surface adhesion molecule; CD34, transmembrane phosphoglycoprotein; CD36, platelet glycoprotein protein 4; CD45, common marker of leukocytes; BCL-xL, anti-apoptotic protein; hemoglobin; FAS; FAS-L; Tf; TfR-1 (or CD71), transferrin receptor 1; TGF-β; activin A; BMP-2, bone morphogenetic protein 2; GDF, growth differentiation factor. Vitamins, trace elements, and iron metabolism proteins necessary for erythropoiesis: vitamin B12, folic acid, copper, iron, ferritin, ferroprotin, hepcidin).