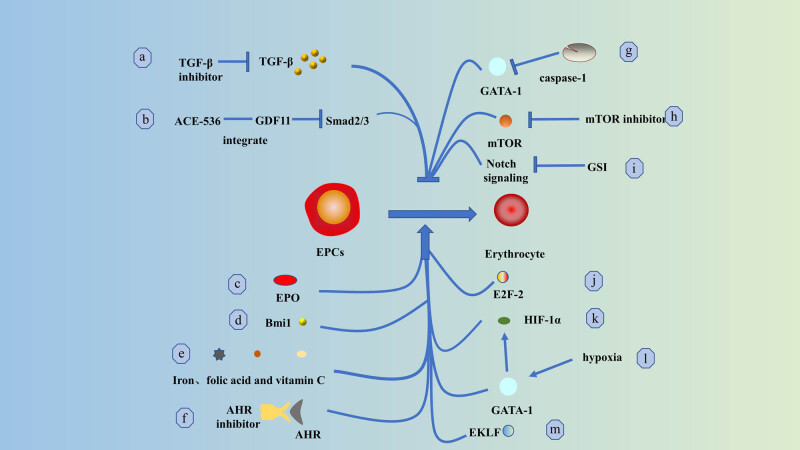
Figure 5.
Critical modulations that promote differentiation of erythroid progenitors: (a) inhibition of TGF-β and (b) binding of GDF11 via ACE-536 effectively rescued differentiation arrest of EPCs; (c) EPO and (d) Bmi1 enhanced differentiation of EPCs; (e) iron, folic acid, and vitamin C also promoted differentiation of EPCs; (f) antagonism of AHR signaling improved hESC-derived erythrocyte production and enhanced terminal differentiation of EPCs; (g) caspase-1 promotes differentiation of EPCs by cleaving GATA1; (h) inhibition of mTOR signaling enhances maturation of EPCs; (i) inhibition of Notch signaling by GSI induces differentiation of EPCs and promotes hemoglobin production; (j) E2F-2 is expressed at high levels in (k). GATA-1 is essential for the differentiation and maturation of late EPCs; (l) hypoxia increases the expression of GATA-1 protein, and overexpression of GATA-1 increases the level of HIF-1α, which promotes the differentiation and maturation of EPCs; and (m) enhanced EKLF in late EKLF of EPCs may promote differentiation of terminal red lineage cells [161,162].