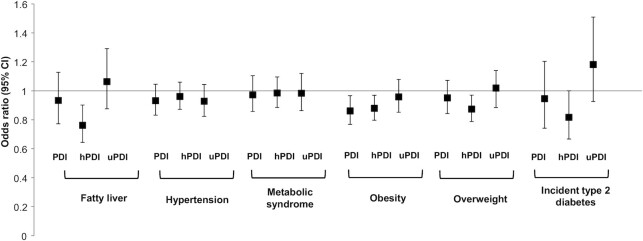
Figure 1.
Likelihood (ORs and 95% CIs) of fatty liver (n = 878; cases = 80), hypertension (n = 891; cases = 357), metabolic syndrome (n = 889; cases = 306), obesity (n = 891; cases = 270), overweight (n = 891; cases = 677), and incident type 2 diabetes (n = 45) per 5-unit increase in the PDI, hPDI, or uPDI score. The multivariable model was adjusted for age, sex, study site, education (Bachelor's degree or higher, yes compared with no), smoking status (never, former, current), alcohol (yes compared with no), family history of diabetes (any first-degree biological relatives), years lived in the United States, exercise (MET-min/week), total energy, diabetes medication use, cholesterol-lowering medication use (yes compared with no), hypertension medication use (yes compared with no), sum of cultural traditional measures, and BMI (except for obesity and overweight) using logistic regression (PROC LOGISTIC, SAS Institute). Fatty liver is defined as liver-spleen attenuation <40 Hounsfield units. Hypertension is defined using the National Cholesterol Education Program criteria as having blood pressure ≥140/90 mmHg or being on medication. Obesity is defined as a BMI ≥27.5 kg/m2. Overweight is defined as a BMI ≥23 kg/m2. Abbreviations: hPDI, healthy plant–based diet index; MET, metabolic equivalents of task; PDI, plant-based diet index; uPDI, unhealthy plant–based diet index.