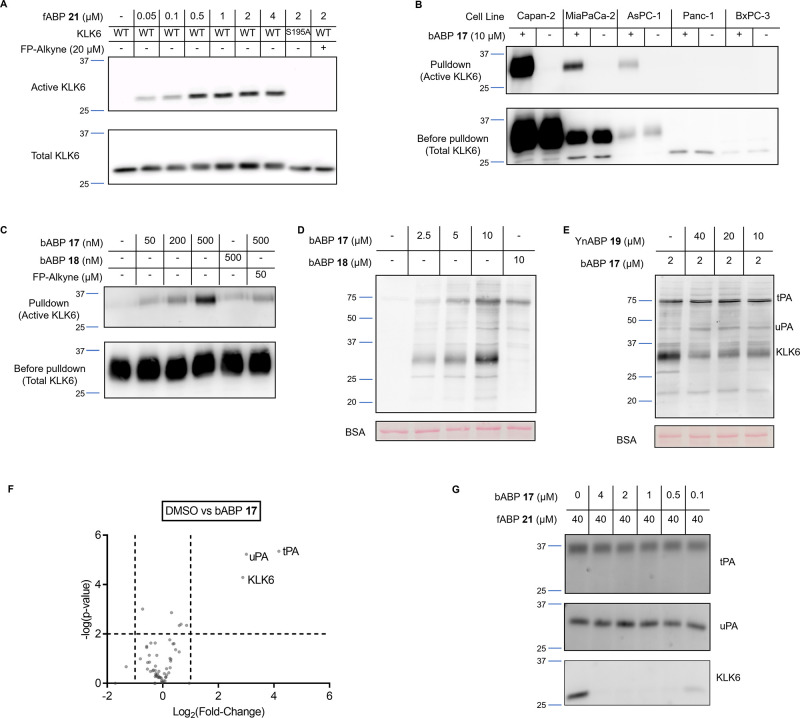
Figure 3.
ABP validation. (A) In-gel fluorescence showing active rhKLK6 labeled by fABP 21 after 1 h incubation. A KLK6 western blot of the gel shows total KLK6. WT = wild-type, S195A = mutated inactive KLK6. (B) KLK6 blot of a pulldown experiment with bABP 17 (IMP-2352) on conditioned media from a panel of PDAC cell lines. Pulldown lanes show enriched proteins after streptavidin binding. Before pulldown shows total KLK6 in each cell line. (C) KLK6 blot of a pulldown experiment with bABP 17 (IMP-2352) at different concentrations on Capan-2 conditioned media. The inactive control 18 shows no labeling. 2 h preincubation with FP-alkyne reduces the labeling of bABP 17 (IMP-2352). (D) NeutrAvidin-HRP blot of Capan-2 media after incubation of compounds 17 (IMP-2352) and 18 for 1 h. (E) NeutrAvidin-HRP blot of Capan-2 media after incubation of the KLK6-selective alkyne probe (YnABP) 19 for 2 h, followed by bABP 17 (IMP-2352) for 1 h. This competition experiment shows that YnABP 19 selectively inhibits KLK6 over tPA and uPA. (F) KLK6 ABP selectivity and on-target validation using LC–MS/MS. Capan-2 conditioned media was treated with bABP 17 (IMP-2352) or DMSO for 1 h, followed by a chemical proteomics workflow to enrich for labeled proteins. The volcano plot compares the changes of protein quantification between DMSO and ABP-treated media, showing the targets of bABP 17 (IMP-2352). (G) Recombinant tPA, uPA, or KLK6 were treated with bABP 17 (IMP-2352) for 2 h, followed by fABP 21 for 1 h. In-gel fluorescence shows selective inhibition of KLK6 over tPA and uPA by bABP 17.