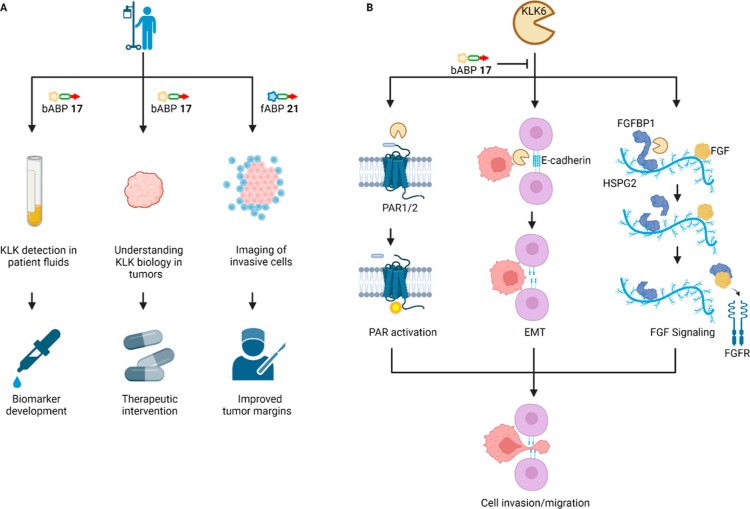
Figure 6.
Summary of the roles of KLK6 in PDAC and potential avenues of further research. (A) Potential future clinical applications of the KLK ABP technology. bABP 17 could be used in patient biofluids or tumor samples to further validate KLK6 as a biomarker or therapeutic target,7 or fABP 21 used as a probe to image active KLK6, for example, in the context of fluorescence-guided surgery. (B) Potential roles for KLK6-mediated invasion and migration in PDAC, which might be targeted for future therapeutic intervention. In addition to activation of PAR49,50,53,54 and cleavage of ECM proteins such as E-cadherin,51,52 we hypothesize a further pro-invasion role for the KLK6–FGFBP1 interaction, whereby the heparin-binding domain drives FGFBP1 in close proximity to FGF on the heparan sulfate chain of HSPG2. FGFBP1 may then be cleaved by KLK6, releasing the active domain that interacts with FGF to promote FGF signaling.