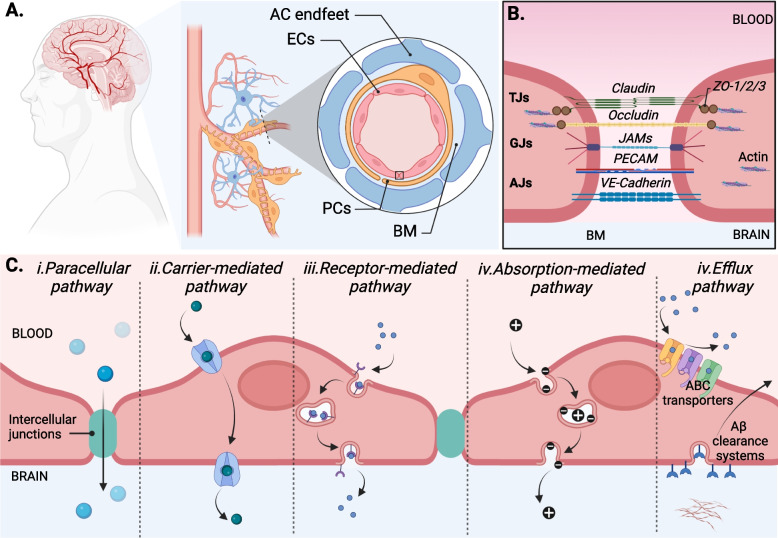
Fig. 1.
Physiological properties of BBB. A. The BBB structure. Schematic diagram of the endothelial cells, pericytes, astrocytes, and basement membrane forming a lumen of brain capillary structures. B. Junctional complexes structure. Single endothelial cell connects by tight junctions (Claudin, Occludin, ZO-1/2/3), gap junctions (JAMs), and adherens junctions (PECAM, VE-cadherin). C. Several different routes of transport across the BBB. i. Paracellular diffusion of gas, water, and small molecules. Transcellular diffusion of high lipid solubility molecules, ii. active transport via carriers of nutrient transport such as glucose, peptide, fatty acid, and nucleic acid, iii. Receptor-mediated transcytosis pathway requires the binding of a receptor on membranous vesicular trafficking. iv. Absorption-mediated transcytosis involves transport through membranous vesicular trafficking via positively charged molecular carriers. v. Active efflux pump systems include ABC transporters, including P-gp, BCRP, and MRP4 inhibit the new metabolites into the brain, whereas Aβ clearance systems reintroduce endogenous metabolites into the bloodstream. ECs represents endothelial cells; PC, pericytes; ACs, astrocytes; BM, basement membrane; TJs, tight junction; GJs, gap junctions; AJs, adherens junction