Extended Data Fig. 10. Proposed model.
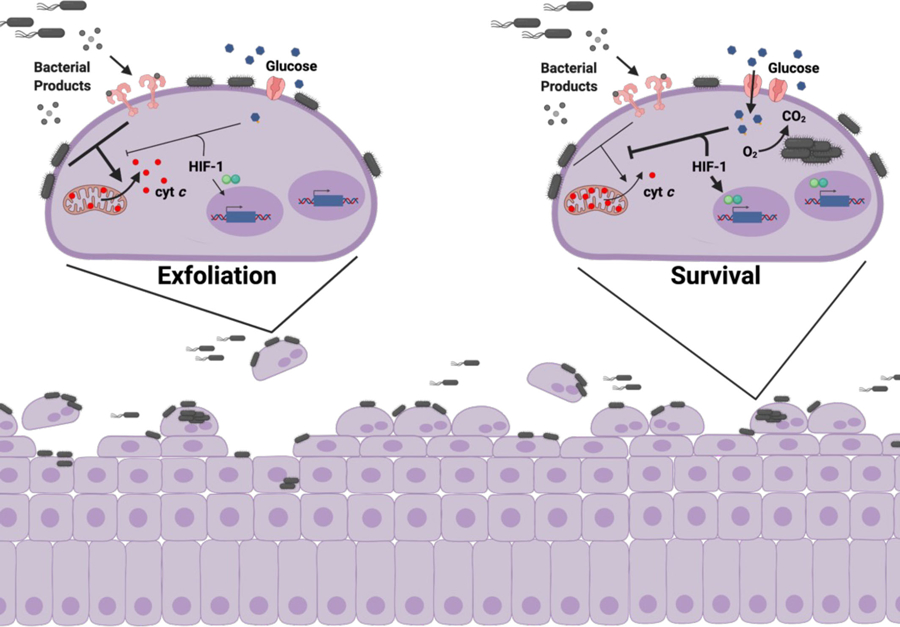
Schematic depicting the proposed model of how intracellular infection modulates urothelial cell metabolism and survival. left, During bladder infection UPEC induces a strong inflammatory response that triggers urothelial cell apoptosis and exfoliation. Urothelial cell exfoliation exposes underlying tissue layers to infection and promotes bacterial persistence in the bladder. right, By consuming oxygen and activating HIF-1 signaling, intracellular bacterial aerobic respiration alters urothelial cell metabolism and antagonizes apoptosis, allowing UPEC to complete its intracellular infection cascade and evade exfoliation.
