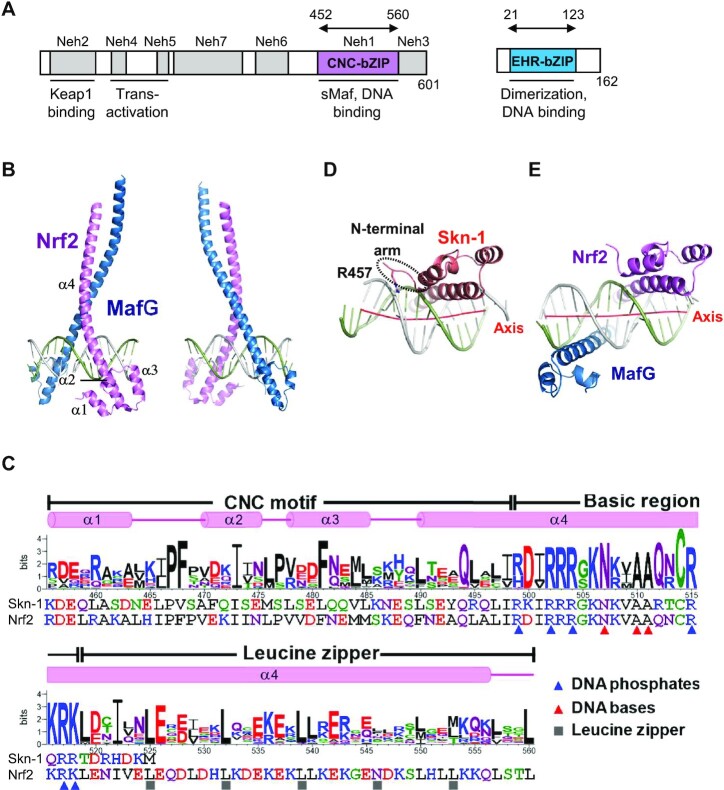
Figure 1.
Structure of Nrf2–MafG–CsMBE1. (A) Conserved regions of Nrf2 and M + afG. Seven conserved regions of Nrf2 designated as Neh (Nrf2-ECH homology) 1–7 are shown along with th + eir functions. Arrows indicate the fragments used for the structural study. (B) Overall structure of the Nrf2–MafG–CsMBE1 complex. (C) Sequence logo created from 34 CNC family proteins, containing homologs of Nrf2, N+-rf1, NF-E2, BACH1 and BACH2. The sequences of human Nrf2 and C. elegans Skn-1 and the Nrf2 secondary structural elements are also shown. The residues interacting with DNA phosphates and bases in the Nrf2–MafG–CsMBE1 complex are indicated by blue and red triangles, respectively. Residues that mediate intermolecular interactions (mainly hydrophobic) at the d positions of the heptad repeats in the leucine zipper region are indicated by gray cubes. (D, E) Bottom views of the Skn-1 DNA-binding domain in a complex with DNA (PDB ID 1SKN) (D) and the Nrf2–MafG–CsMBE1 complex (E). The red lines show the helical axes of the bound DNA double helices in each complex.