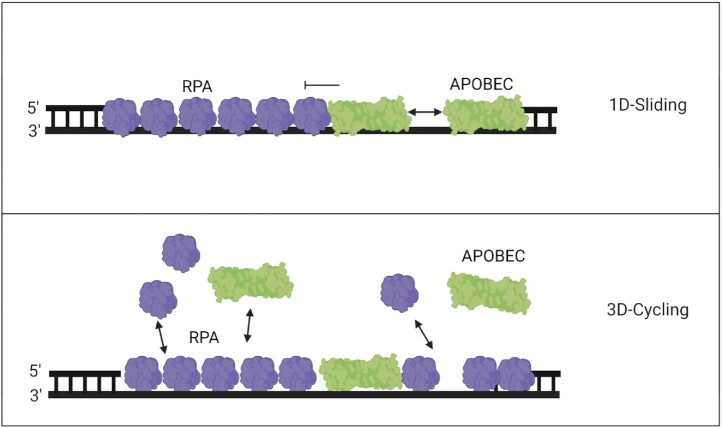
Figure 5.
Model of competitive binding of APOBECs and RPA. The tight binding of RPA on ssDNA acts as a roadblock, limiting APOBECs from catalyzing processive deaminations. (Top panel) This effectively prevents competitive exchange of RPA with APOBECs that can only slide along the DNA backbone, leading to lowered APOBEC specific activity. (Bottom panel) Bound RPA can undergo exchange with free RPA through facilitated dissociation allowing an opportunity for APOBECs to bind. Three-dimensional rapid cycling on/off ssDNA enables APOBECs to compete with RPA for ssDNA as both proteins exchange between bound and free states. The displacement of RPA enables deamination activity from A3s that do not require processive sliding, but instead locate cytosines by cycling on/off the ssDNA.