Figure 1.
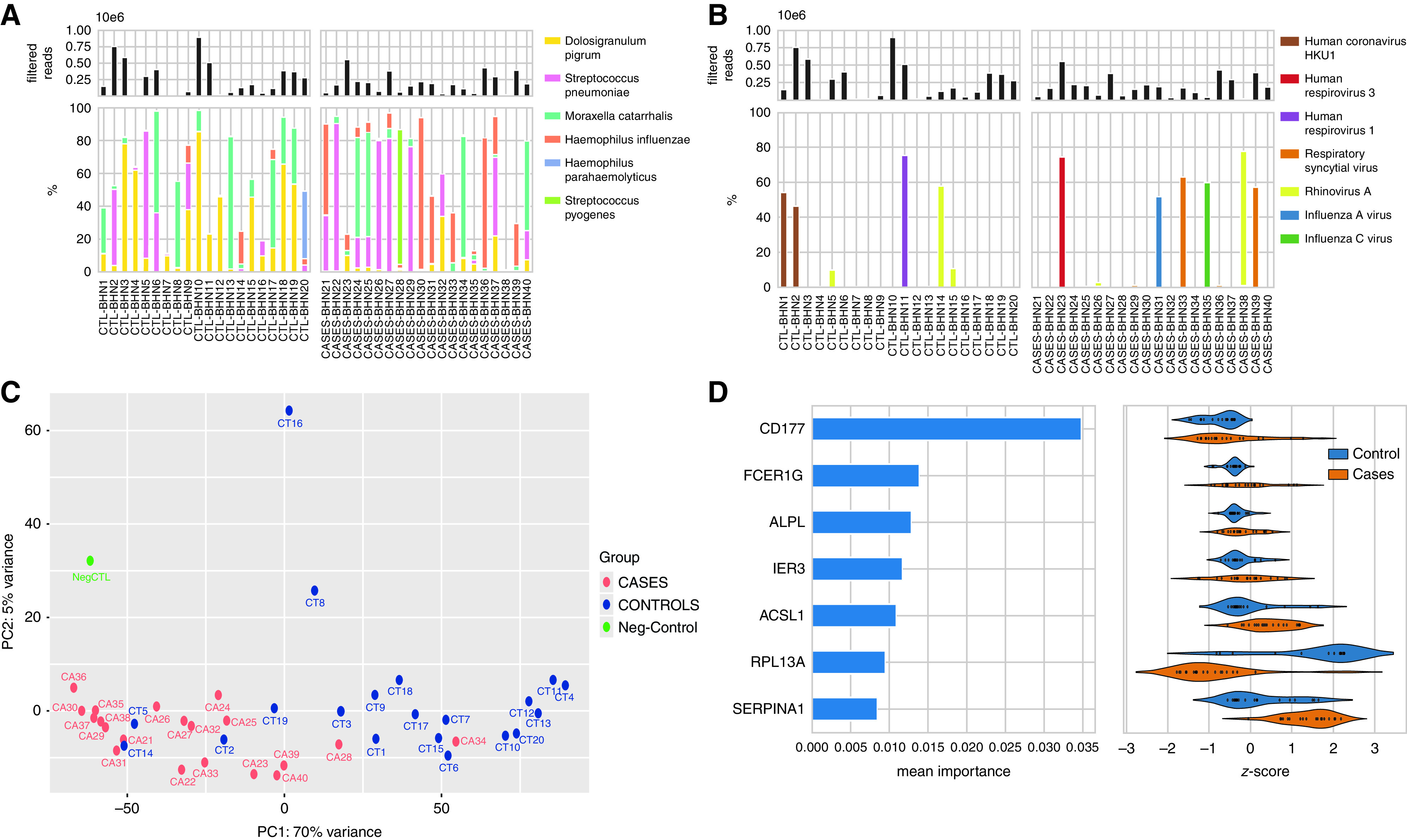
(A) The top panel shows the total filtered non-rRNA (non-ribosomal RNA) reads (bacterial, viral, and human non-rRNA reads) across the samples. The bottom panel shows the percentage of reads that belong to the most abundant bacterial taxa identified. (B) The top panel shows the total filtered non-rRNA reads, and the bottom panel shows the percentage of reads that belong to the most abundant viral species. (C) The principal component analysis (PCA) was performed on human reads using variance stabilizing normalization from DESeq2, R package using the plotPCA function that includes the top 500 genes selected by highest row variance. The normalization employed considers the sequencing depth and the RNA composition and uses the median of ratios method. Blue color circles indicate the control subjects, and red color circles show the cases. Names have been shortened to read CTRL-BHN1 = CT1 and Case-BHN21 = CA21, etc. (D) Random forest feature importance averaged over 20 model runs (left) for the main features in the best-performing classification model, and their corresponding transcription degrees expressed as z-scores in cases and control subjects. Z-scores were calculated by subtracting the mean and dividing by the standard deviation for each sample, resulting in samples having a mean of 0 and a variance of 1. PC1 = principal component 1; PC2 = principal component 2.
