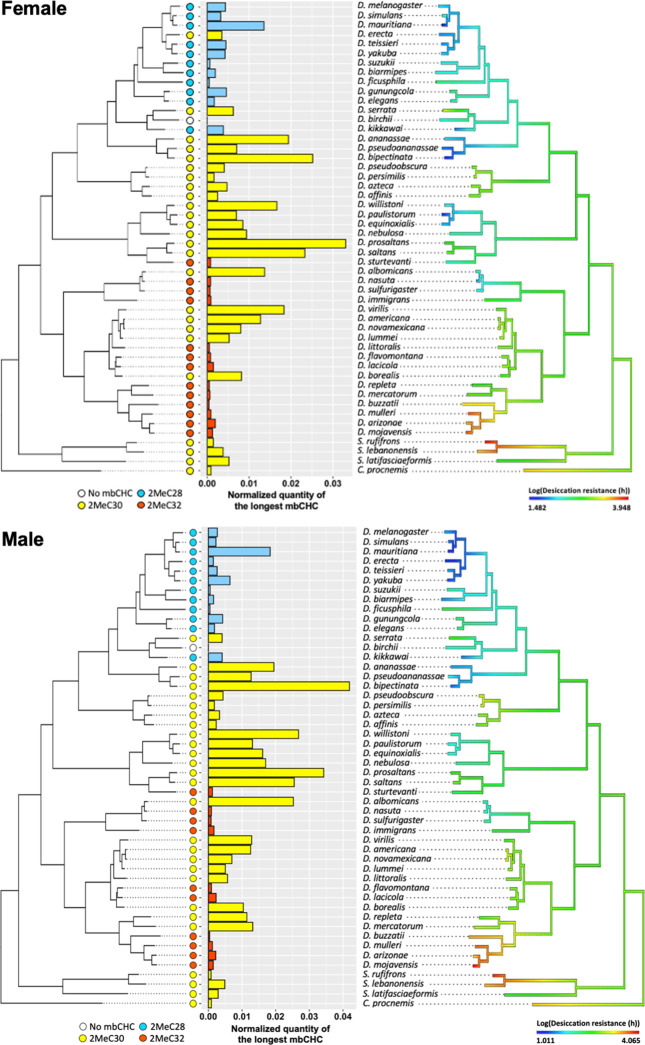
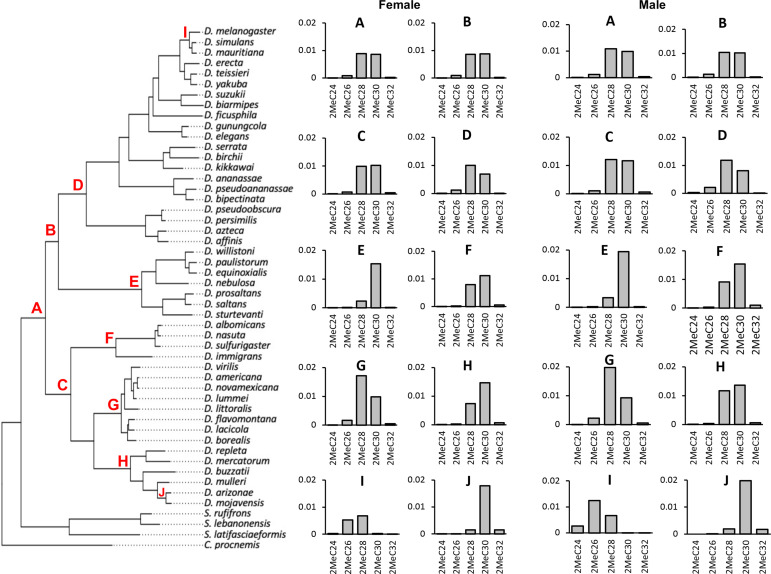
Figure 6. Evolution of longer mbCHCs is significantly correlated with evolution of higher desiccation resistance.
Patterns in the normalized quantities of the longest mbCHCs and desiccation resistance for females (top) and males (bottom) were listed across the phylogeny of the 50 Drosophila and related species. Phylogenetic Generalized Linear Square (PGLS) analysis between the longest mbCHCs and desiccation resistance showed both the higher quantity and longer length of the longest mbCHC affect desiccation resistance (interaction term, Female: t = 3.5, p < 0.001; Male: t = 2.2, p = 0.03).