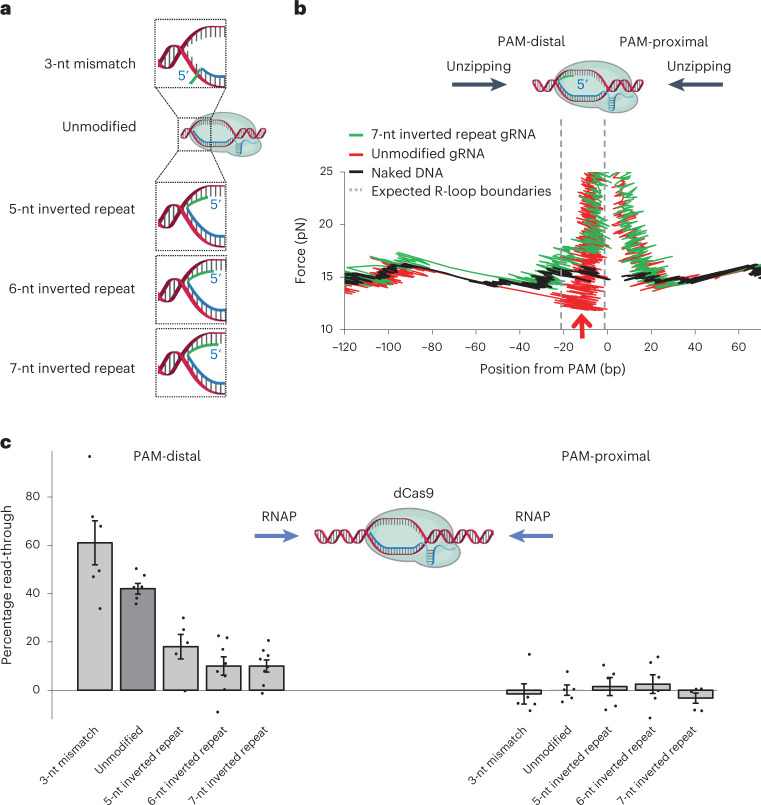
Fig. 4. Modulation of transcription read-through of a bound dCas complex via gRNA modifications.
a, Cartoons depicting the four types of modified gRNA. b, Representative unzipping mapper traces that highlight the force signature difference between a bound dCas9 containing a modified gRNA with a 7-nt inverted repeat (IR) and a bound dCas9 containing an unmodified gRNA. Vertical dashed lines bracket the position of the gRNA-DNA hybrid. Naked DNA traces are shown in black. The red arrow indicates the location of the unzipping force dropping below the naked DNA baseline for the trace with an unmodified gRNA. c, Transcription read-through efficiency for RNAP encountering a bound dCas from either the PAM-distal side or the PAM-proximal side. DNA was always unzipped in the same direction as RNAP translocation. For each sample chamber, both control traces and noncontrol traces were taken to obtain the read-through efficiency for that chamber. Each type of experiment was repeated using n biologically independent sample chambers: dCas9 PAM-distal, n = 6 (3-nt mismatch), n = 6 (unmodified), n = 5 (5-nt IR), n = 8 (6-nt IR) and n = 8 (7-nt IR); dCas9 PAM-distal, n = 5 (3-nt mismatch), n = 5 (unmodified), n = 5 (5-nt IR), n = 6 (6-nt IR) and n = 5 (7-nt IR). Read-through values were calculated for each sample chamber (black dots) and the mean value and s.e.m. of these repeats are also shown. Source data containing traces for b and transcription read-through values for c are provided.