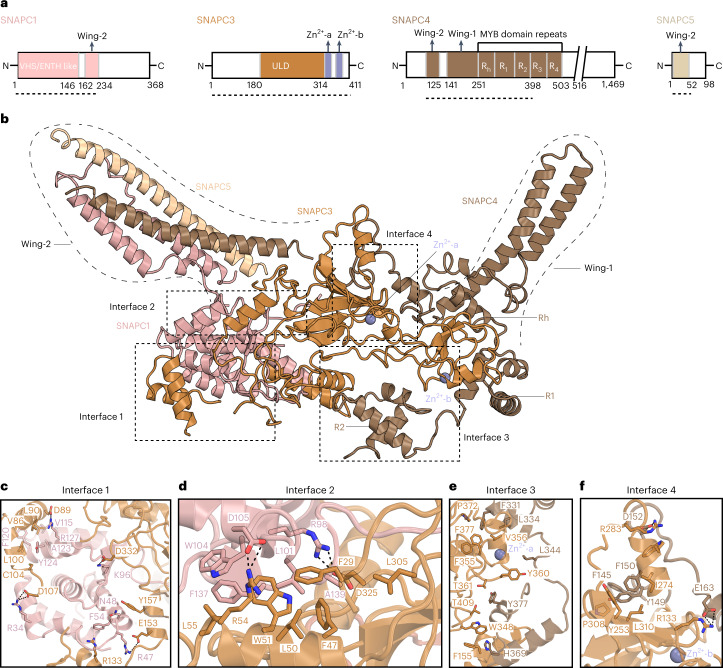
Fig. 3. Structure of SNAPc.
a, Two-dimensional (2D) domain schematics of individual SNAPc subunits. The regions visible in the 3D structure are marked by dotted lines. b, SNAPc structure in cartoon representation. Domain nomenclature and colors are as in a. Dashed boxes indicate the interfaces between the subunits. c,d, Close-up view of interfaces 1 and 2 that are formed between SNAPC1 (pink) and SNAPC3 (orange). The residues V115, F120, A123 and Y124 of SNAPC1 and V86, L90, L100 and C104 of SNAPC3 form mainly hydrophobic interactions, whereas ionic interactions are formed between R34, R47, K96 and R128 of SNAPC1 and D89, D107, E153 and D332 of SNAPC3. F54 of SNAPC1 and R133 of SNAPC3 form a cation-pi interaction, and N49 of SNAPC1 and Y157 of SNAPC3 form polar contacts. Similarly, in interface 2, SNAPC1 L101, W104, F137 and A139 form hydrophobic contacts with F47, L50, W51, L55 and L305 of SNAPC3. Salt bridges involving R98 and D105 of SNAPC1 and R54 and D325 of SNAPC3 fortify interface 2. e,f, Interfaces 3 and 4 between SNAPC3 (orange) and SNAPC4 (chestnut brown). In interface 3, SNAPC3 residues F155, W348, F355, V356, Y360, T361, P372, F377 and T409 form the bulk of hydrophobic contacts with F331, L334, L344 and H369 of SNAPC4 (Fig. 3e). Likewise, in interface 4, the residues Y253, I274, W277, P308 and L310 make hydrophobic contacts with the amino acids F140, Y149, F150 and F176 of SNAPC4. Additional salt bridges are formed by R133 and R283 of SNAPC3 with D152 and E153 of SNAPC4. The Zn-fingers (ZF-1 and ZF-2) of SNAPC3 are in close proximity to the interfaces 3 and 4 and would be important for the structural integrity of this complex. The residues involved in these protein–protein interaction surfaces are highly conserved across metazoans (Extended Data Figs. 7 and 8).