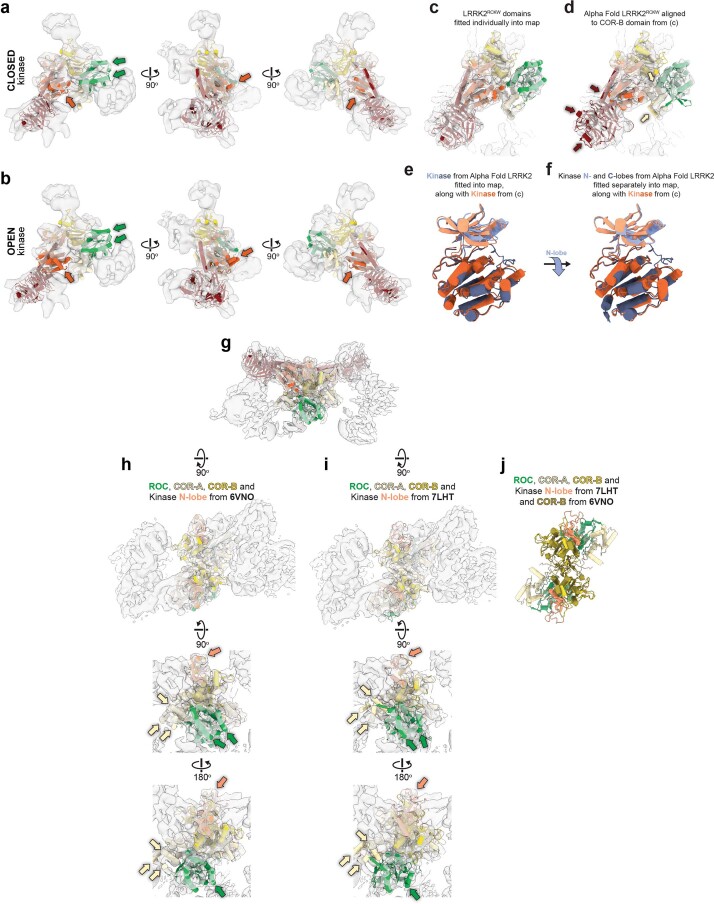
Extended Data Fig. 3. Structural analysis of microtubule-associated filaments of LRRK2RCKW[I2020T].
a, A model for LRRK2RCKW[I2020T] with a closed kinase, obtained by docking the individual domains into the cryo-EM map of LRRK2RCKW[I2020T] filaments obtained in the presence of MLi-2, was docked into a cryo-EM map (7 Å) of filaments obtained in the absence of the inhibitor (Extended Data Fig. 2). b, A model for LRRK2RCKW with an open kinase (PDB:6VNO) was docked into the same map. The colored arrows in (a) and (b) highlight structural elements in the model that protrude from the density when the kinase is in an open conformation. c, The LRRK2RCKW domains (ROC, COR-A, COR-B, Kinase N-lobe, Kinase C-lobe, WD40) (PDB:6VNO) were fitted individually into one of the monomers in the cryo-EM map of microtubule-bound LRRK2RCKW[I2020T] formed in the presence of MLi-2. d, The LRRK2RCKW portion of the AlphaFold model of LRRK2 was aligned to the COR-B domain in (c) and is shown here inside the same cryo-EM map. The colored arrows highlight regions where part of the model protrudes from the density. (Note: there is no arrow pointing to the loop in the ROC domain as this loop was not seen or modeled in the microtubule-bound structure). e, The kinase from the AlphaFold model of LRRK2 was fitted into the cryo-EM map (same as in (d)) and is shown here superimposed on the N- and C-lobes of the kinase as fitted in (c). Note that while the C-lobes superimpose well, the N-lobe fitted individually in (c) is more closed than that modeled in the AlphaFold LRRK2. f, The N- and C-lobes of the kinase from the AlphaFold LRRK2 model were now fitted individually into the cryo-EM map (as in (c)) and are shown superimposed on the N- and C-lobes of LRRK2RCKW from (a). The blue arrow between panels (e) and (f) highlights the downward movement of the N-lobe of AlphaFold’s LRRK2 when the two lobes are fitted individually into the cryo-EM map. g, The LRRK2RCKW domains (ROC, COR-A, COR-B, Kinase N-lobe, Kinase C-lobe, WD40) (PDB:6VNO) were fitted individually into the central dimer of the cryo-EM map of a tetramer of microtubule-bound LRRK2RCKW[I2020T] obtained in the presence of MLi-2. h, i, Different closeup views of the map in (g), showing either (h) the ROC, COR-A, COR-B and kinase N-lobe from the LRRK2RCKW model (PDB:6VNO), or (i) the corresponding portion from the structure of full-length LRRK2 (PDB:7LHT) docked as a single body into the cryo-EM map. The colored arrows highlight parts of the model that fit the cryo-EM density better when the domains are fitted in individually (h) rather than as a rigid body (i). j, Superposition of the model used in (i) and the COR-B domain from (h) to show that the differences among the ROC, COR-A and N-lobe of the kinase between the two models ((h) and (i)) is not due to major differences at the COR-B:COR-B interface, which is similar.