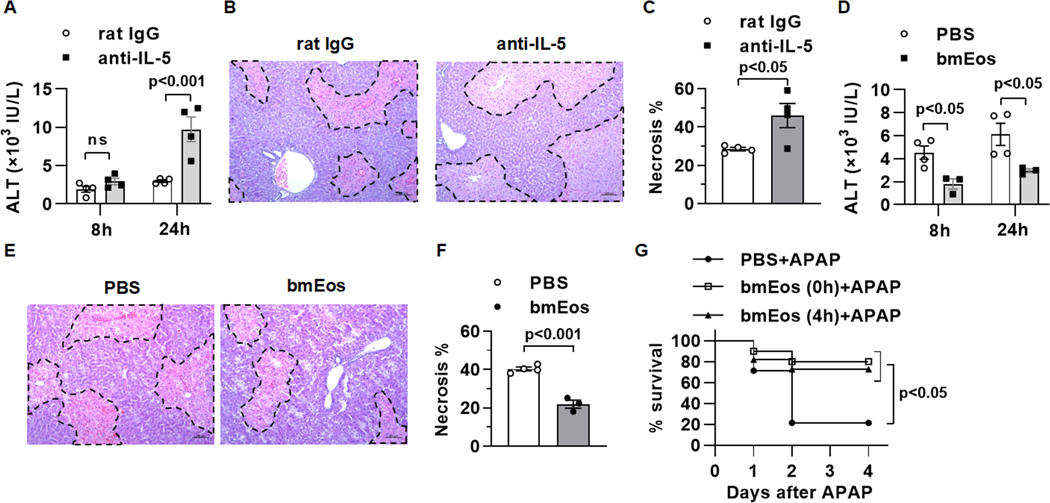
Fig. 1. Eosinophils infiltrate the liver and exert a profound protection against AILI.
(A to C) WT mice were i.p. injected with anti-IL-5 antibody (200μg/mouse) to deplete eosinophils or rat IgG as control at 18h prior to APAP treatment (n=3–4/group). (A) Serum levels of ALT were measured at 8 and 24h after APAP treatment. (B and C) Liver necrosis (scale bars, 100μm) was evaluated and quantified at 24h after APAP treatment. (D to F) WT mice were adoptively transferred with PBS or WT bmEos immediately prior to APAP treatment (n=3–4/group). (D) Serum levels of ALT were measured at 8 and 24h after APAP treatment. (E and F) Liver necrosis (scale bars, 100μm) was examined and quantified at 24h after APAP treatment. (G) WT mice were treated with a lethal dose of APAP (600mg/kg). At 0h and 4h after APAP treatment, mice were i.v. injected with PBS or bmEos (7.5×106, n=10–14/group). The survival rates were recorded within 4 days after APAP treatment. Two-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test was performed in A and D. Two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test was performed in C and F. Long-rank (mantel-COX) test was performed in G.