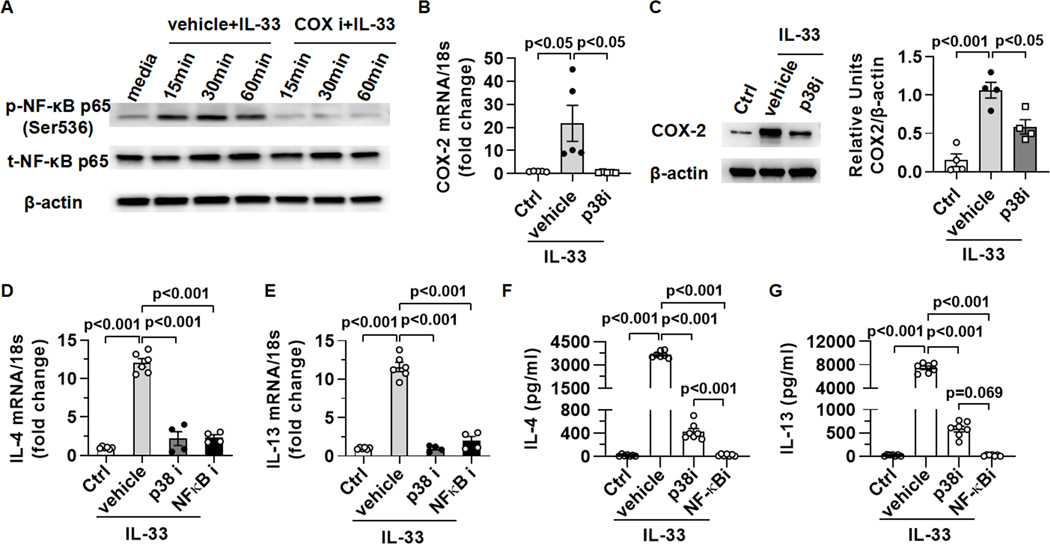
Fig. 5. The signal pathway of p38-COX-NF-κB is critical for IL-4/IL-13 production by eosinophils in response to IL-33.
(A) WT bmEos were treated with IL-33 (20ng/ml) in presence of sc-560 and celecoxib (50μM each, COXi ) or vehicle (10μl DMSO) in vitro for various times. Expression levels of phosphorylated-p65 and total-p65 were measured by Western blotting. (B and C) WT bmEos were treated with vehicle (1μl DMSO) or a p38 inhibitor (SB203580, 10μM) for 1h before stimulation by IL-33 (20ng/ml). WT bmEos without any treatment were regarded as control (Ctrl). (B) After 2h of IL-33 treatment, mRNA levels of COX-2 were measured by qPCR. (C) After 6h of IL-33 treatment, expression levels of COX-2 were measured by Western blotting. (D to G) WT bmEos were treated with vehicle (1μl DMSO), a p38 inhibitor (SB203580, 10μM), or a NF-κB inhibitor (BAY11–7821, 10μM) for 1h, then the cells were washed and stimulated with IL-33 (20ng/ml). WT bmEos without any treatment were regarded as control (Ctrl). (D and E) After 4h of IL-33 treatment, mRNA levels of IL-4 and IL-13 were measured by qPCR. (F and G) After 24h of IL-33 treatment, the concentrations of IL-4 and IL-13 in supernatants were measured by ELISA. One-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test was performed in B to G.