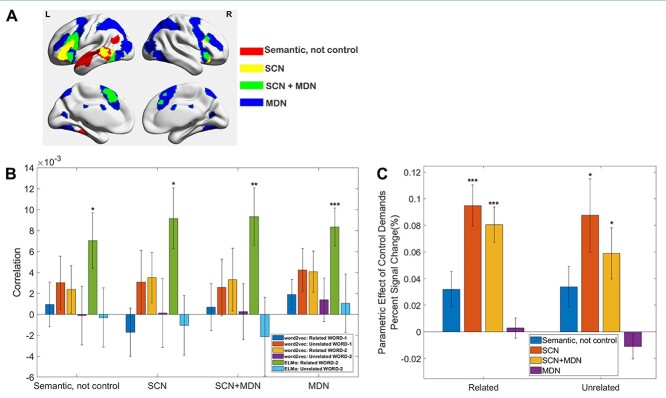
Fig. 4.
a) Functional networks: (i) semantic not control, (ii) within the SCN but outside multiple-demand cortex (DMN), (iii) within both SCN and MDN, and (iv) falling in MDN regions not implicated in semantic cognition. b) Neural representation of context-free and context-dependent meaning in functional networks. Positive correlations were found for context-dependent meaning of WORD-2 for trials judged to be related in all four networks. c) Univariate parametric effects in four functional networks showing modulation of the BOLD response according to control demands: the weaker associative strength for trials judged to be related was associated with the higher activation, while the stronger associative strength for trials judged to be unrelated was associated higher activation. SCN and regions falling within both SCN and MDN showed significantly higher activation for those trials with weaker associations and consequently higher controlled retrieval demands. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Bonferroni correction was applied.