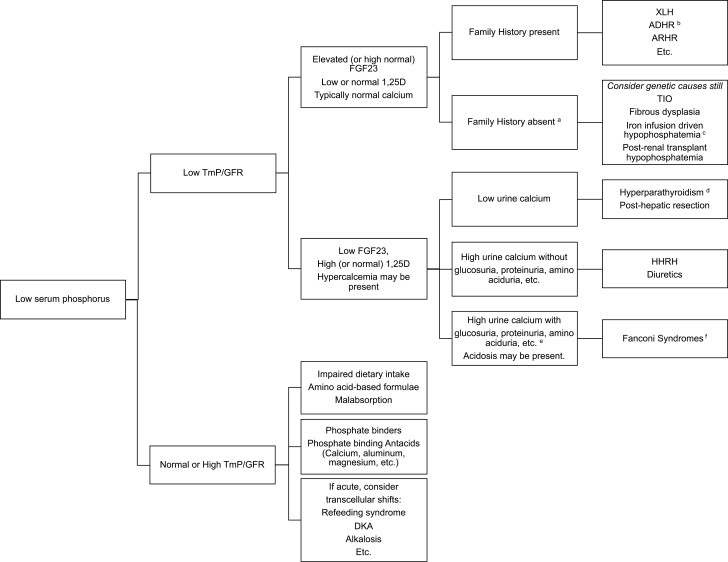
Figure 1.
Algorithm for assessing causes of hypophosphatemic rickets. Note that before applying this algorithm, the calciopenic causes of rickets (such as vitamin D deficiency, etc., must first be excluded). The calciopenic forms are often marked by hypocalcemia along with marked elevation of PTH. Once calciopenic forms are excluded, evaluation for causes of hypophosphatemia is pursued beginning with TmP/GFR. aConsider genetic causes even without family history. bIron deficiency itself triggers hypophosphatemia in ADHR. cIron infusions especially iron carboxymaltose or polymaltose can also trigger hypophosphatemia, likely through impaired cleavage of FGF23. dFGF23 may be high in hyperparathyroidism. eHypercalciuria may not always be present in tubulopathies. fNon-FGF23–mediated causes of hypophosphatemia may still result in high FGF23 concentrations if moderate to severe chronic kidney disease develops.