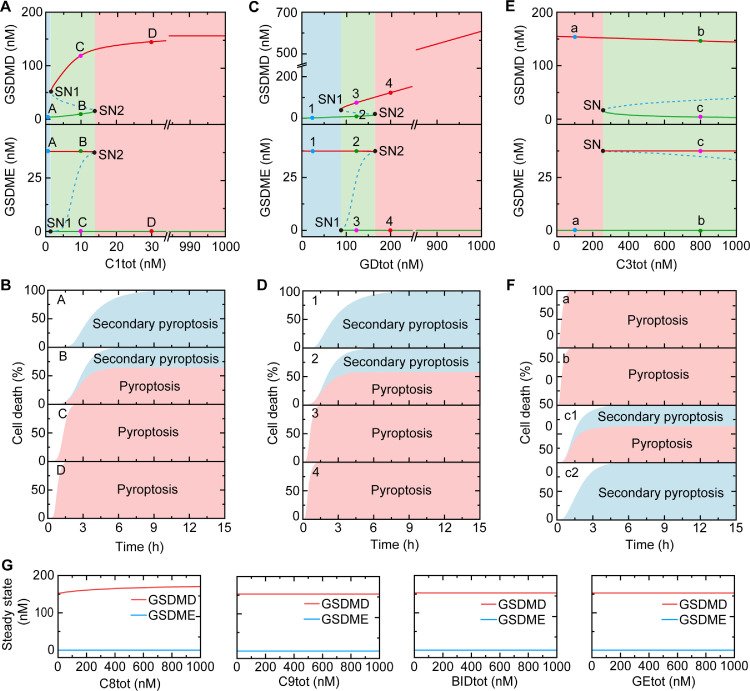
Fig. 3.
Roles of constituent levels in death mode switching. (A) Bifurcation diagrams of GSDMD and GSDME as function of caspase-1 expression level (C1tot). Stable and unstable steady states are indicated by solid and dashed lines, respectively. (B) The contribution proportions of pyroptosis and secondary pyroptosis to cell death for points A–D in Fig. 3A, respectively. (C) Bifurcation diagrams of GSDMD and GSDME as function of GSDMD expression level (GDtot). (D) The contribution proportions of pyroptosis and secondary pyroptosis to cell death for points 1–4 in Fig. 3C, respectively. (E) Bifurcation diagrams of GSDMD and GSDME as function of caspase-3 expression level (C3tot). (F) The contribution proportions of pyroptosis and secondary pyroptosis to cell death for points a–c in Fig. 3E, respectively. (G) Bifurcation diagrams of GSDMD and GSDME as function of the expression level of caspase-8 expression level (C8tot), caspase-9 (C9tot), Bid (BIDtot), and GSDME (GEtot). In Fig. 3A, C, and E, the green areas are the bistability regions, while pink and blue areas correspond to monostability regions, respectively. In Fig. 3B, D and F, the pink and blue areas correspond to pyroptosis and secondary pyroptosis, respectively.