FIGURE 1.
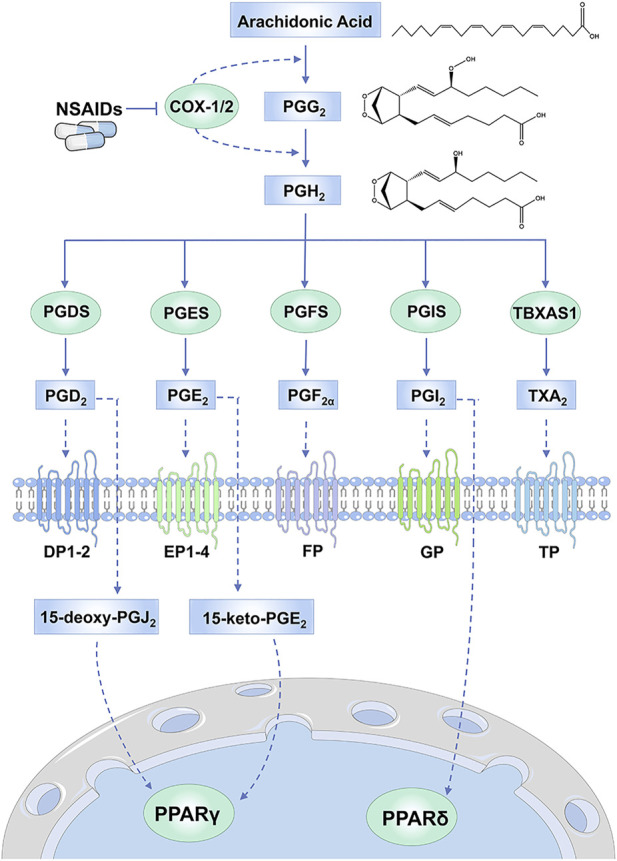
Synthetic and signal transduction pathways of prostaglandins. Arachidonic acid can be transformed into PGG2 and PGH2 via COX enzymes, which can be inhibited by NSAIDs. Then PGH2 is converted into various prostaglandins via specific synthases. Prostaglandins then exert their actions by activating receptors on cell membranes, including DP1-2, EP1-4, FP, IP and TP. Nuclear receptors such as PPARγ and PPARδ can also be activated by prostaglandins or their metabolites. Abbreviations: PGG2, prostaglandin G2; PGH2, prostaglandin H2; PGDS, PGD synthase; PGES, PGE synthase; PGFS, PGF synthase; PGIS, PGI synthase; TBXAS1, TXA synthase; peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR).
