Figure 5 |. Glucocorticoids modulate T cell activity.
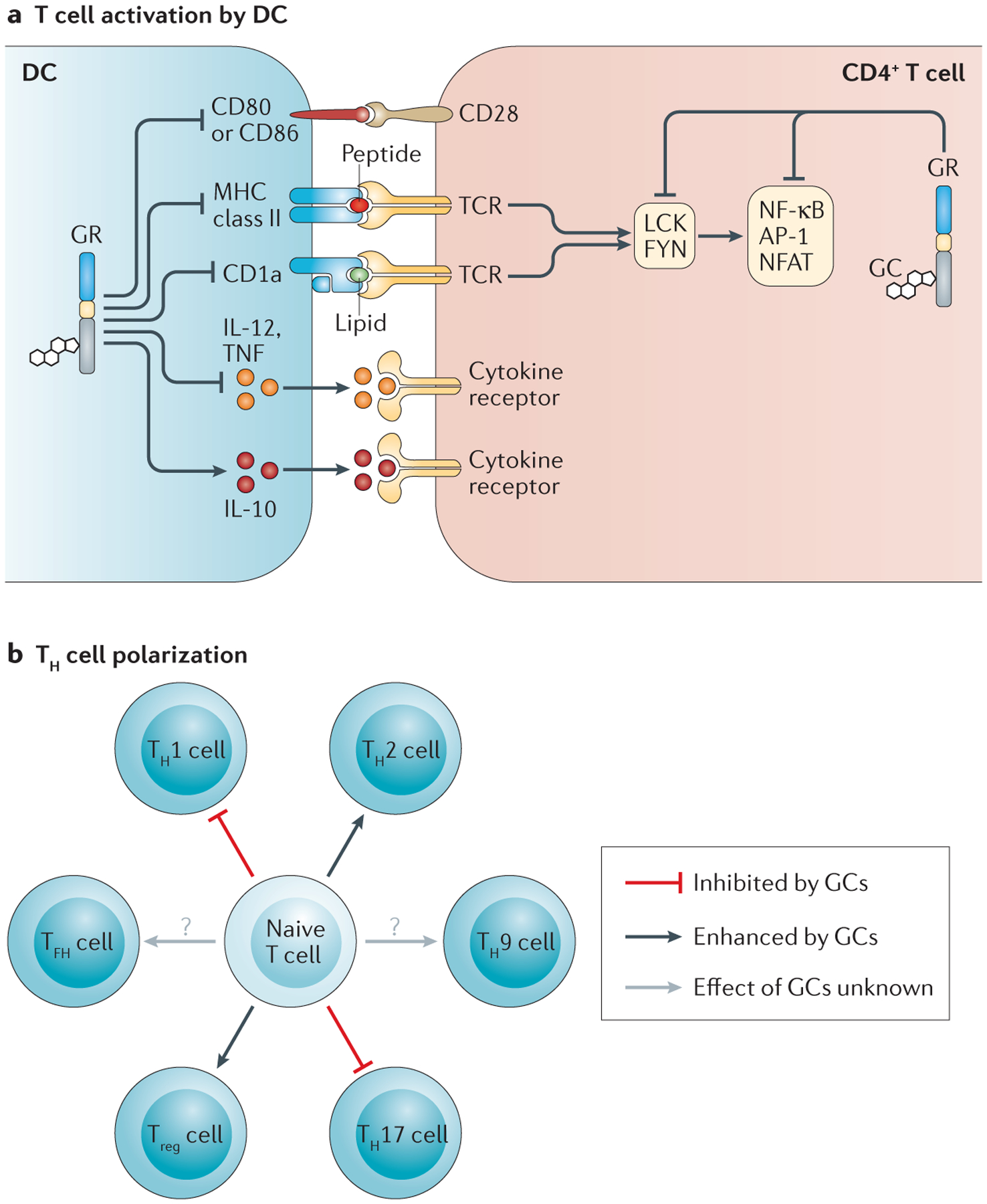
a | Glucocorticoids (GCs) suppress CD4+ T cell activation indirectly by modulating dendritic cell (DC) function (antigen presentation, co-stimulation and cytokine production) and directly by regulating T cell receptor (TCR) signalling. b | GCs influence the polarization of T helper (TH) cells, favouring the differentiation of TH2 cells and regulatory T (Treg) cells over that of TH1 cells and TH17 cells. The effects of GCs on the differentiation of TH9 cells and T follicular helper (TFH) cells require further investigation. AP-1, activator protein 1; GR, GC receptor; IL, interleukin; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T cells; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; TNF, tumour necrosis factor.
