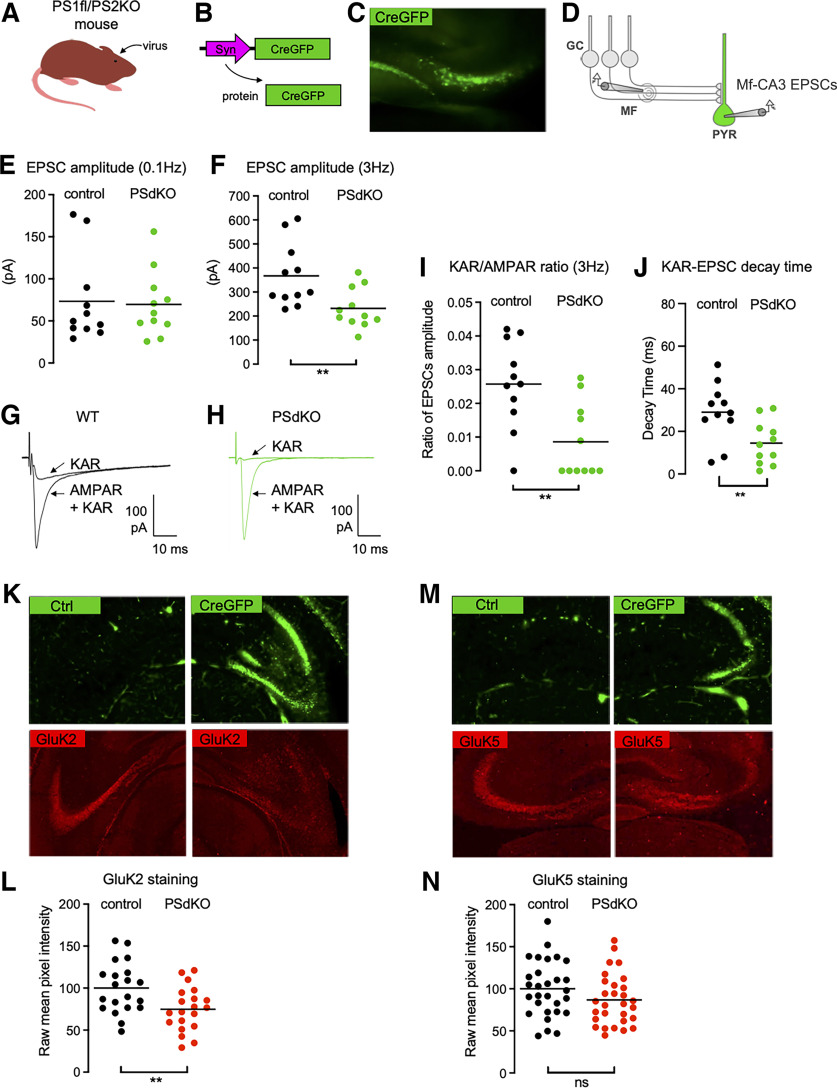
Figure 3.
Impaired synaptic expression and function of KARs in the absence of PS. A, Cartoon representing the generation of PSdKO CA3 cells. Cre recombinase-expressing viruses are injected into the CA3 region by stereotaxic surgery. B, Scheme representing the lentiviral vector to express Cre fused to GFP in CA3 pyramidal neurons. C, Representative image of the CA3 region targeted with a virus expressing Cre-GFP. D, Scheme representing the stimulation of Mf that evokes EPSCs recorded in PsdKO CA3 pyramidal neurons (PYR) identified with GFP. E, F, Scatter plots with averages of the EPSC amplitude recorded at 0.1 Hz (E) or 3 Hz (F) demonstrate that synaptic basal transmission (at 0.1 Hz) is not altered in the postsynaptic PSdKO condition, whereas synaptic transmission is decreased at 3 Hz (n = 11/genotype), indicating impaired frequency facilitation. G, H, Representative traces of EPSCs recorded at 3 Hz in WT mice (G) or in postsynaptic PSdKO mice (H) under conditions where both AMPAR and KAR currents are active or when KAR currents have been pharmacologically isolated. I, Amplitude of KAR-EPSCs normalized to AMPAR-EPSCs recorded at 3 Hz. The relative amplitude of KAR-EPSCs is significantly lower in the postsynaptic PSdKO condition. J, Average decay times of KAR-EPSCs are markedly decreased in PsdKO conditions mice. K, GluK2 staining in the CA3 region of PS1fl/PS2 conditional KO mice targeted (right) or not (left) with a Cre-GFP-expressing virus. The staining is decreased in the postsynaptic PSdKO condition. L, Quantification of raw mean pixel intensity in the stratum lucidum region of images, as in J. Data were normalized to the mean intensity of the WT condition. M, GluK5 staining in the CA3 region of the PSdKO mice is similar to WT mice. N, Quantification as in K shows no statistically significant decrease of GluK5. **p < 0.01. ns = non-significant.