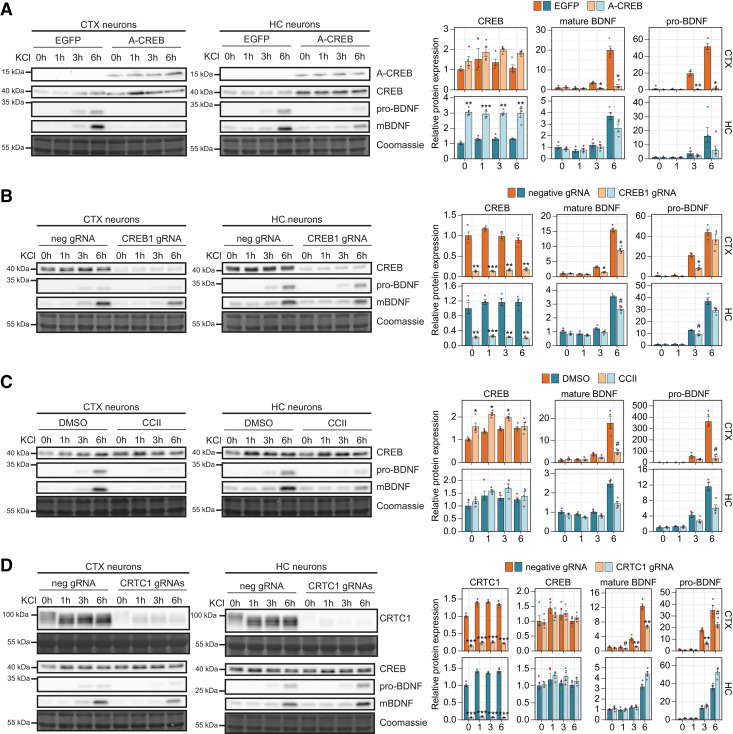
Figure 6.
Regulation of activity-dependent BDNF protein levels by CREB family transcription factors and coactivators in cortical and hippocampal neurons. Cultured rat cortical (CTX) or hippocampal (HC) neurons were left untreated (0 h) or treated with 25 mm KCl at 8 DIV for the indicated time (1, 3, or 6 h). Regulation of activity-dependent BDNF protein expression was analyzed using lentiviruses encoding EGFP- or A-CREB (A), dCas9-KRAB along with negative control guide RNA (neg gRNA) or gRNA targeting CREB1 promoter (CREB1 gRNA; B), or preteated with CBP-CREB interaction inhibitor (CCII; C), or with dCas9-KRAB along with gRNA targeting CRTC1 promoter (CRTC1 gRNA; D). A-CREB, CREB, CRTC1, pro-BDNF, and mature BDNF (mBDNF) protein levels were measured using Western blotting and representative Western blotting images in cortical and hippocampal neurons are shown on the left, with Coomassie staining as a loading control. The pro-BDNF and mature BDNF levels were measured from the same membrane and their protein levels are shown using the same exposition time. The bar graphs on the right show densitometric analysis of the expression levels of CREB, CRTC1, pro-BDNF, and mature BDNF normalized with Coomassie signal. The protein levels in untreated control neurons (EGFP- or neg gRNA-expressing neurons or neurons treated with DMSO) were taken as 1. Error bars represent mean ± SEM of four biological replicates (n = 4), and individual data points of each biological replicate are shown with dots. Statistical significance is shown relative to the respective protein levels in control cells at the respective time point of KCl treatment in respective culture. Group averages and exact p-values are shown in Extended Data Figure 6-1. #p < 0.1, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, paired two tailed t test, corrected for multiple comparisons using Holm method.