Figure 1.
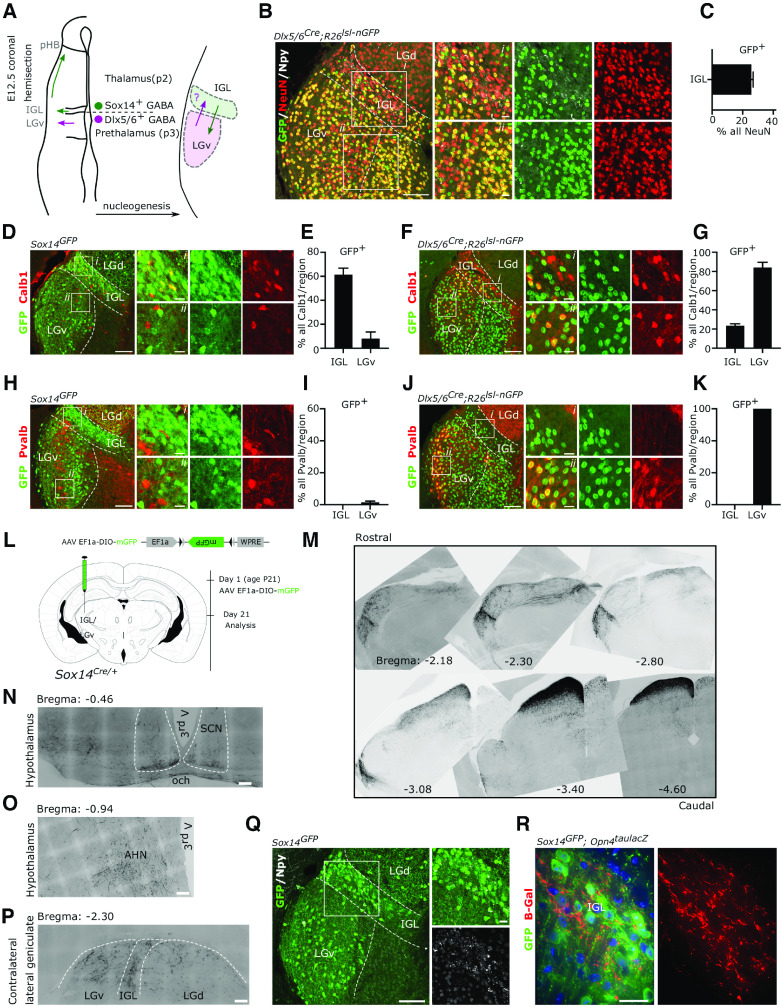
Thalamic and prethalamic lineages in the IGL/LGv complex. A, Schematic representation of the left diencephalon along the coronal plane at the time of peak embryonic neurogenesis (E12.5) illustrating the two main sources of GABAergic neurons for the IGL and the LGv. Radial migration of prethalamic (p3) GABAergic precursors (magenta) generates the bulk of the LGv, while radial migration of thalamic (p2) GABAergic precursors (green) generate the bulk of the IGL. Tangential migration of thalamic GABAergic precursors contributes to the formation of the pHB and to the cellular complexity of the LGv. The possibility of a complementary contribution of prethalamic GABAergic precursors to the IGL is tested using the prethalamic GABAergic driver Dlx5/6Cre. B, Representative image illustrating the presence of neurons (NeuN+) with prethalamic origins (GFP+) in the IGL. Note the presence of NeuN+GFPneg neurons in the LGv, consistent with the thalamic origin of some LGv neurons and of NeuNnegGFP+ glia in the LGd. C, Quantification of the fraction of IGL neurons with prethalamic origin. D, E, Representative images and quantification of the mosaic expression of the calbindin protein (Calb1) among thalamic (Sox14GFP/+) lineages in the IGL and LGv. F, G, Representative images and quantification of the mosaic expression of Calb1 in prethalamic (Dlx5/6Cre;R26lsl-nGFP) lineages in the IGL and LGv. H–K, Representative images and quantification of the expression of Pvalb in thalamic and prethalamic lineages of the IGL and the LGv. L, Schematic illustration of timeline of the AAV injection strategy used to label axonal projections of the Sox14+ IGL/LGv neurons in the adult brain. M, Inverted gray scale images from representative rostrocaudal levels of the IGL/LGv, demonstrating the widespread presence of dark GFP labeled fibers (see L for strategy) projecting away from the IGL/LGv and toward other diencephalic and mesencephalic structures. N–P, Higher magnification images from the experiment in L showing the presence of sparse GFP-labeled fibers in the SCN, the AHN and the contralateral geniculate. Q, an illustrative example of the location of thalamic Sox14+ neurons in the IGL and the LGv at three weeks of age. R, Example image showing the incoming ipRGC axons (b-gal) in the region occupied by Sox14+ neurons in the IGL using the Opn4taulacZ/+;Sox14GFP/+ double transgenic mouse.