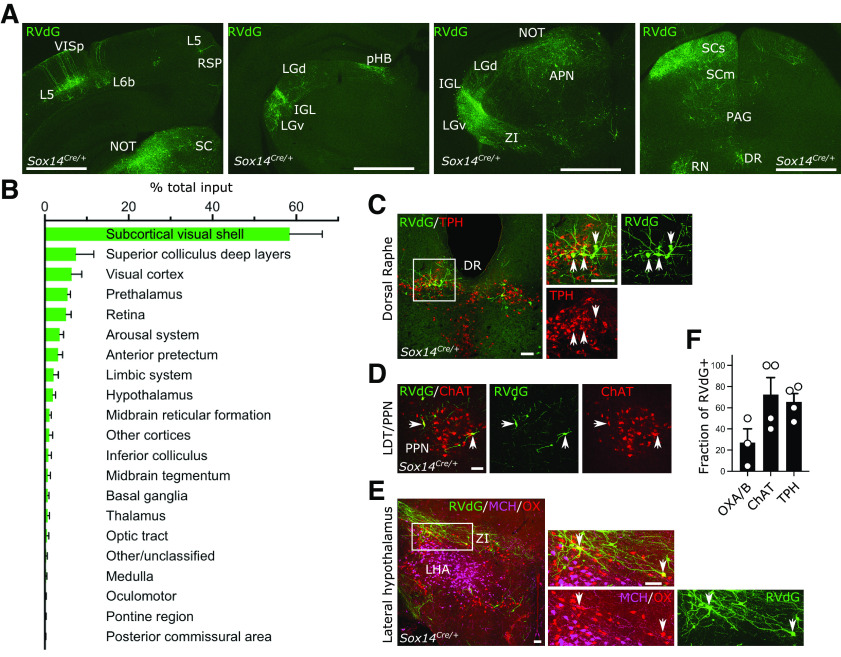
Figure 6.
Brain-wide input to the Sox14+ neurons in the IGL/LGv. A, Representative coronal sections showing brain-wide distribution of inputs to Sox14+ neurons in IGL/LGv. Most inputs to Sox14+ IGL/LGv can be observed in areas with visual functions (VISp, SCs, NOT, IGL/LGv). Green, GFP from RVdG. Scale bars: ∼1 mm. B, Quantification of inputs to Sox14+ neurons in IGL/LGv, shown as percentage of total inputs (mean ± SEM; n = 4 mice). See also Extended Data Table 6-1 for anatomic classification based on previously published work (Paxinos and Franklin, 2001). C, D, Representative coronal sections showing inputs from the ascending arousal system. Not all RVdG-infected cells (GFP+, green) are co-stained with the anti-tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH; red) antibody in dorsal raphe (DR) or the anti-choline acetyltransferase (ChAT; red) in pedunculopontine nucleus (PPN). Scale bars: 100 mm. E, Representative coronal section showing inputs from the lateral hypothalamus. In the lateral hypothalamic area, a small proportion of RVdG-infected cells (GFP+, green) are co-stained with the anti-orexinA/B antibody (OX, red), but none with the anti-melanin concentrating hormone antibody (MCH, magenta). Scale bars: 100 µm. F, Quantification of the fraction of RVdG-labeled neurons that expressed the indicated markers (mean ± SEM).