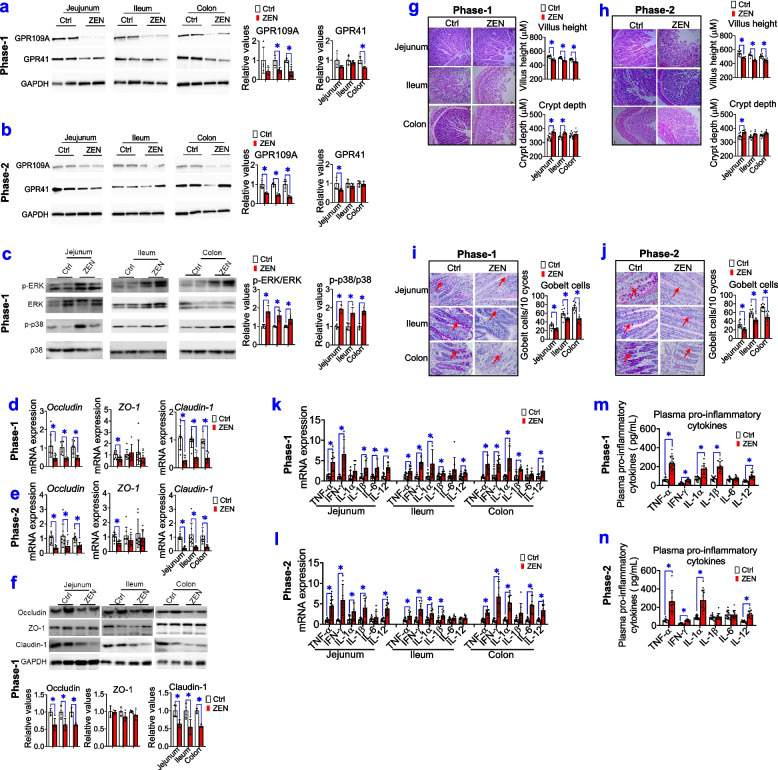
Fig. 5.
ZEN-induced toxicity impairs the intestinal barrier by altered microbial metabolites. a, b Representative Western blots and its quantification of SCFAs receptors (e.g., GPR109A and GPR41) in the jejunum, ileum, and colon of pigs, during phase-1 pigs (a) and phase-2 pigs (b), between the Ctrl group and ZEN group. The GAPDH is used as the loading Ctrl (n=4). c Representative Western blots and its quantification of the ERK1/2 and p38 signalling pathway (n=4). d–f The mRNA expression (d, e, n=8), representative Western blots and its quantification (fn=4) of tight junction markers (e.g., occludin, claudin-1, and ZO-1) in the jejunum, ileum, and colon. g, h The intestinal morphology of pigs during phase-1 (g) and phase-2 (h). The left of panels g and h: representative light micrographs of a cross-section from the jejunum, ileum, and colon under ×40 magnification. The scale bar represents 200 μm. On the right of panels g and h: the quantification of villus height and crypt depth (n=8). i, j Periodic acid–Schiff staining (PAS) staining for goblet cells in the jejunum, ileum, and colon. On the left of panels i and j: representative staining for goblet cells in the intestine (The arrows indicate positive goblet cells). Scale bars: 100 μm. The right of panels i and j: the quantification of immunoreactive goblet cells using digital image analysis (n=8). k, l The mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the jejunum, ileum, and colon (n=8). m, n The levels of plasma pro-inflammatory cytokines in pigs (n=8). Bar values are means ± SEM. *P < 0.05