Fig. 7. Elevated anti-PDIA3 autoantibodies in the sera of patients diagnosed with T2D, autoimmune hepatitis, and autoimmune cholangitis.
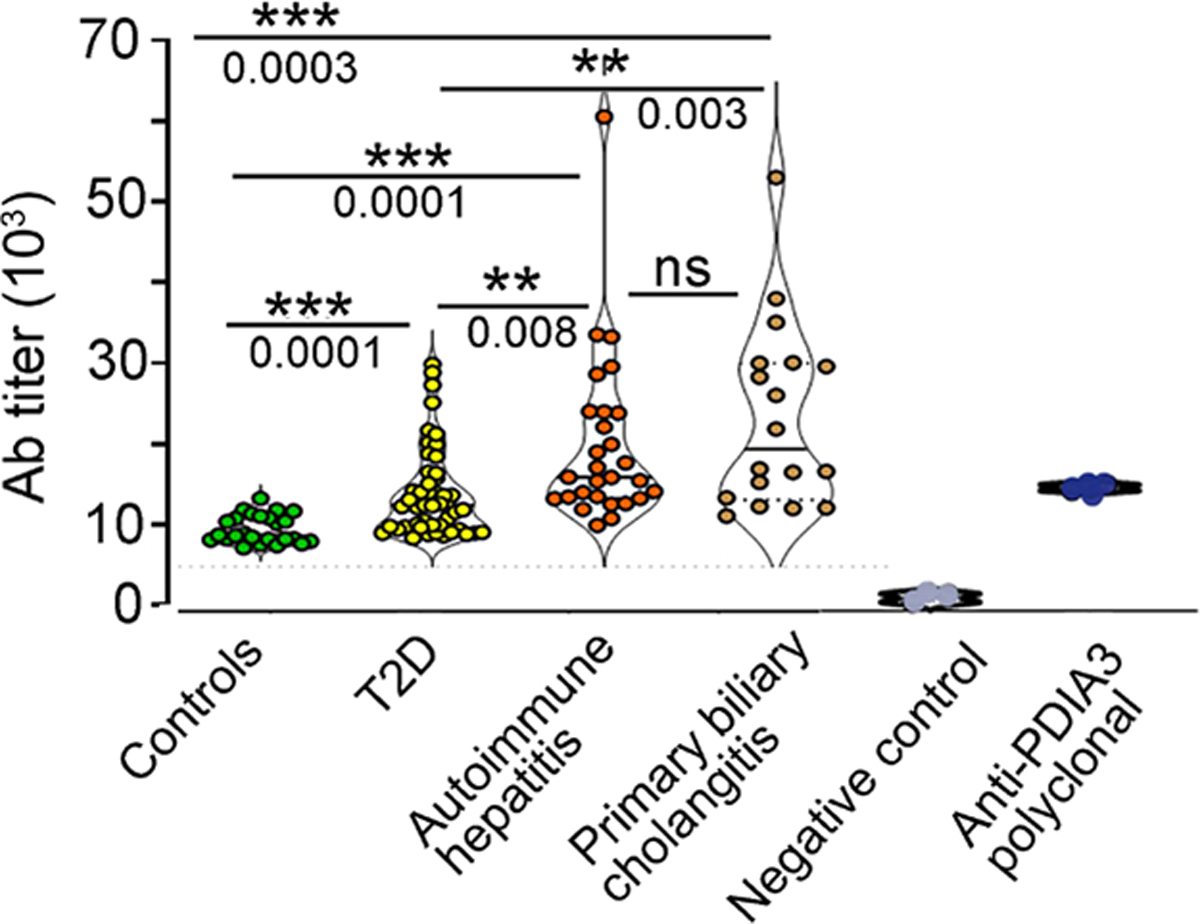
Sera, collected from 25 healthy age- and sex-matched controls, 48 patients with a diagnosis of T2D, 28 subjects with a diagnosis of AIH, and 18 subjects with PBC, were tested in ELISA against the full-length human PDIA3 protein. Antibody titers were quantified in each subject, and each dot symbol represents the average of three technical replicates. Statistical analysis for each serum and the representative binding curves are presented in fig. S7 and table S7. The statistical significance was determined with one-way ANOVA including mixed-effects model restricted maximum likelihood (REML) followed by multiple comparisons performed with uncorrected Fisher’s LSD test (***P < 0.0001, **P < 0.001, and *P < 0.01). For specificity testing, commercially available polyclonal anti-PDIA3 antibody was used as positive control, whereas PBS buffer served as negative control.
